EPA RCRA ID: OHD032271975
On this page:
- Latest News
- Cleanup Status
- Facility Description
- Contaminants at this Facility
- Institutional/Engineer Controls
- Enforcement and Compliance
- Related Information
- Contacts for this Facility
Congress amended the Resource Conservation and Recovery Act (RCRA) in November 1984, expanding the Act's cleanup provisions and prompting EPA and its state partners to develop the RCRA Corrective Action Program. The program oversees the investigation and cleanup of nearly 4,000 hazardous waste sites across the country, including many with risks comparable to Superfund sites.
Latest News
The public comment period for the Nucor Steel Marion, Inc. facility Statement of Basis closed on May 18, 2023. EPA received several public comments, which EPA will review and respond to in our Final Decision and Response to Comments document. This document will also include the final remedy selected for the facility. EPA will publish the Final Decision and Response to Comments document on this website when it is final.
Information pertaining to the Statement of Basis is below. For additional information, please see the Administrative Record.
- Cleanup Fact Sheet(PDF)
- Statement of Basis (PDF)
- Nucor Steel – Marion, OH – Proposed Cleanup (YouTube)
Cleanup Status
Nucor conducted several investigations to determine
- Where wastes were generated on-site.
- If there were hazardous waste releases to the environment.
- The nature and extent of the hazardous waste contamination.
In 1989 an initial investigation was conducted, followed by
- A hydrogeologic assessment.
- Several years of soil and groundwater sampling investigations.
- Soil gas sampling to determine vapor intrusion potential in site soils.
Based on the results of the investigations, eight areas at the Nucor facility underwent cleanup. Nucor performed interim measures to reduce levels of contamination and risk to on-site workers.
The interim measures completed include:
- Baghouse Area: excavation and disposal of soil contaminated with electric arc furnace dust, petroleum hydrocarbons, and arsenic.
- Settling Basin Shipping Area: excavation and disposal of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon-contaminated soils.
- Billet Yard: excavation/removal and disposal of polychlorinated biphenyl-contaminated soils, concrete, and water.
- Former Press Pit: removal of residual free product consisting of lubrication oil.
- Former Underground Storage Tank Area: excavation and disposal of soil contaminated by diesel fuel.
- Former Oil Room: in-place chemical and biological reduction of trichloroethene in shallow groundwater.
- Former Dumping Area: excavation and disposal of lead-contaminated soil.
- Former Paint Pit: excavation and disposal of soil contaminated with paint waste.
Areas remain on-site that require additional remedial measures be completed to manage contaminated soil and groundwater and protect human health and the environment. EPA issued a Statement of Basis that explains the proposed remedy for contaminated soil, groundwater, and vapor intrusion potential as part of the Agency’s public participation responsibilities under RCRA. EPA will select a final remedy for the facility after the public comment period has ended and any information provided by the public has been reviewed and considered. EPA may modify the proposed remedy or select another remedy based on new information or public comments.
Cleanup Activities Pertaining to the Entire Facility
| Action | Status | Date of Action |
|---|---|---|
| Human Exposure Under Control Human Exposure Under Control(CA725) | ||
| Groundwater Migration Under ControlGroundwater Migration Under Control (CA750) | ||
| Remedy DecisionRemedy Decision (CA400) | ||
| Remedy ConstructionRemedy Construction (CA550) | ||
| Ready for Anticipated Use Ready for Anticipated Use (CA800) | ||
| Performance Standards AttainedPerformance Standards Attained (CA900) | ||
| Corrective Action Process TerminatedCorrective Action Process Terminated (CA999) |
For definitions of the terms used, hover over or click on the term.
Link to a larger, interactive view of the map.
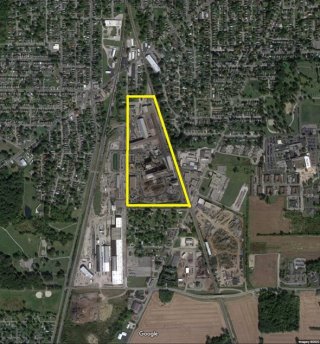
The Nucor Steel facility has operated as a steel mill since 1915, when it was run by Pollak Steel. In 1974, Armco Steel purchased the facility. In 1981, financial difficulties forced a temporary shutdown. In 1983, Marion Steel took ownership and resumed operations. In June 2005, Nucor purchased the facility and continues to operate it to this day. The steel mill utilizes two electric arc furnaces to produce reinforcement bars, fence posts, and angle iron.
The steel mill is located on the southwest side of Marion, Ohio. It occupies approximately 40 acres. It is surrounded by industrial property to the west and east, and mixed commercial and residential to the east, north, and south.
Contaminants at this Facility
Contaminants of concern remaining at the facility include:
Soil:
Lead
Groundwater:
Polychlorinated biphenyls, chromium, lead, volatile organic compounds, non-aqueous phase liquids, and unformulated lubrication oil.
Vapor intrusion:
Tetrachloroethene and trichloroethene.
Institutional and Engineering Controls at this Facility
The remedy proposed in the Statement of Basis requires Nucor to establish an environmental covenant to restrict the land use of the Nucor property to industrial use now and in the future. The environmental covenant will also include a site restriction to ensure future occupants are protected from exposure via vapor intrusion. It will also prohibit the use of groundwater at the facility as a source for drinking water.
Additionally, the remedy proposed in the Statement of Basis requires Nucor to comply with a Soil and Groundwater Management Plan (SGMP). The SGMP is a written health and safety plan that describes contaminants that could be encountered during construction work at the facility. It includes requirements for personal protective equipment to be used. It stipulates the soil, groundwater, and air monitoring to be performed, and waste handling and disposal procedures to follow during excavation work.
Institutional and Engineering Controls help ensure human exposure and groundwater migration are under control at a cleanup facility. Where control types have been reported by states and EPA in EPA’s RCRAInfo, they are shown below. Not all control types are needed at all facilities, and some facilities do not require any controls. Where there are blanks, the control types may not be needed, may not be in place, or may not be reported in RCRAInfo.
Are Controls in Place at this Facility?
| Control(s) Type | Control(s) in Place? | Areas Subject to Control(s) | Documents available on-line: | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Institutional ControlsNon-engineering controls used to restrict land use or land access in order to protect people and the environment from exposure to hazardous substances remaining in the site/or facility. (CA 772) | Informational DevicesInformational Devices (ID) | |||
| Governmental Controls (GC) | ||||
| Enforcement and Permit Tools (EP) | ||||
| Proprietary ControlsProprietary Controls (PR) | ||||
Engineering ControlsEngineering measures designed to minimize the potential for human exposure to contamination by either limiting direct contact with contaminated areas or controlling migration of contaminants. (CA 770) | Groundwater ControlGroundwater Control (GW) | |||
Non-Groundwater | ||||
For definitions of the terms used, hover over or click on the term.
Enforcement and Compliance at this Facility
EPA’s Office of Enforcement and Compliance Assurance (OECA) provides detailed historical information about enforcement and compliance activities at each RCRA Corrective Action Site in their Enforcement and Compliance Historical Online (ECHO) system.
RCRA Enforcement and Compliance Reports from ECHO
Related Information
For more information about this facility, see these other EPA links:
- Information about this facility submitted to EPA under different environmental programs as reported in EPA’s Facility Registry Services
- Cleanups in My Community provides an interactive map to see EPA cleanups in context with additional data, and lists for downloading data
- Search RCRA Corrective Action Sites provides a search feature for Corrective Action Sites
Documents, Photos and Graphics
Contacts for this Facility
- Monica Onyszko (onyszko.monica@epa.gov), EPA Project Manager, 312-353-5139.
- Francisco Arcaute (arcaute.francisco@epa.gov), Public Affairs Specialist, 312-886-7613.
All of the states in EPA Region 5 are authorized to implement Corrective Action Programs. As of the end of Fiscal Year 2015, EPA Region 5 had 864 sites listed on the 2020 Corrective Action Baseline.
For further information on this corrective action site, use the Contact Information for Corrective Action Hazardous Waste Clean Ups listings that are accessible through Corrective Action Programs around the Nation.
