DMAP GraphQL API
On this page
- About this page
- Overview
- Quickstart
- Query basics
- Filtering
- Joins
- Subqueries
- Pagination
- Ordering results
- Grouping results
- Variables
- Export formats
- Limitations
- Related Envirofacts API tools
- Help and feedback
About this page
This page documents the DMAP GraphQL API, a GraphQL-like query service that supports complex queries (including joins and aggregations) across Envirofacts database tables.
Overview
The DMAP GraphQL API allows you to query Envirofacts tables using a GraphQL-compliant syntax. The service endpoint is:
https://data.epa.gov/dmapservice/query
DMAP is not a full GraphQL implementation (see Limitations), but it supports a rich query language for selecting fields, filtering, joining, ordering, grouping, and exporting results.
Quickstart
DMAP queries follow a simple pattern: choose a schema, a table, and one or more fields. Tables are referenced as schema__table (double underscore).
Example
query quickstart { icis__icis_activity_report (limit: 10) { activity_name activity_status_desc actual_begin_date_fy } }
This query selects activity_name, activity_status_desc, and actual_begin_date_fy from the icis_activity_report table in the icis schema, limited to 10 records.
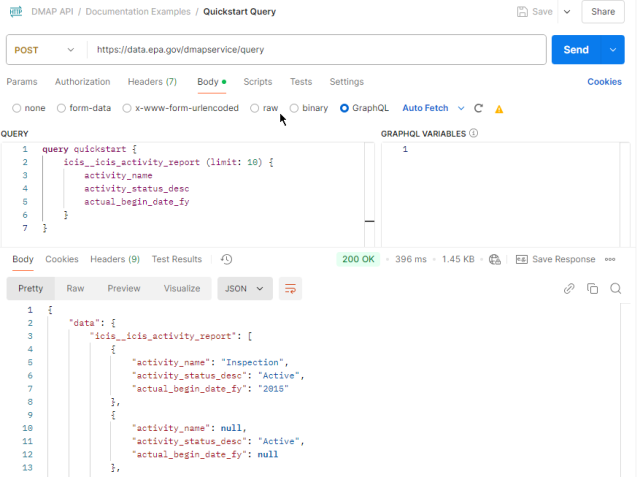
Performing a query
You can run DMAP queries using many GraphQL-capable tools, including user interfaces such as Postman or Thunder Client.
Postman example
Create a new POST request to https://data.epa.gov/dmapservice/query. In the request body, select a GraphQL body type (or raw JSON if your client requires it), paste your query, and send the request to view the response.
Query basics
Schema and table
A schema and table must be supplied when querying data. The format is schema__table (note the double underscore). For example, to query the ref_city table in the icis schema, use icis__ref_city.
Table aliases
You can rename a table in the resulting data set with the alias argument.
query aliasQuery { icis__ref_facility_type(alias: fac_types) { facility_type_desc facility_type_code } }
In this example, the ref_facility_type results are returned under the fac_types element in the output. The table alias is not used when exporting results in the GraphQL export format.
Selecting fields
At least one field must be supplied (unless querying only an aggregation). Fields are listed inside the table block.
query fieldsQuery { icis__ref_naics { naics_code naics_desc status_flag } }
All fields
To return all fields in a table, use the special field __all_columns__.
query allFields { icis__ref_naics { __all_columns__ } }
Field aliases
To rename a field in the output, use the alias argument on the field.
query fieldAlias { icis__ref_naics { naics_code naics_desc (alias: description) status_flag } }
Field casts
To cast a selected field to a different type when it is returned, add the cast attribute to the field.
query fieldCast { icis__icis_activity_report (limit: 20) { activity_name activity_status_desc fiscal_year (cast: "text") } }
Reference: valid cast types
- date
- decimal
- float
- integer
- number
- text
Aggregations
To perform an aggregation (for example, count, min, max), include an aggregate block.
query aggregateCount { icis__icis_activity_report { aggregate { count } } }
Aggregation parameters
Some aggregations support additional parameters such as distinct, fields, and alias.
query aggregateCountDistinct { icis__icis_activity_report { aggregate { count (distinct: true, fields: ["actual_end_date_fy", "activity_name"], alias: "field_count") } } }
Reference: available aggregation methods
- count
- Purpose: returns the total count of records.
- Format:
count
- max
- Purpose: returns the maximum value of a column.
- Format:
__max__column_name
- min
- Purpose: returns the minimum value of a column.
- Format:
__min__column_name
Distinct
To return distinct records, add distinct: true to the primary table call.
query distinctQuery { icis__ref_naics (distinct: true) { naics_code naics_desc (alias: description) status_flag } }
Functions
User functions
To select a user-defined function in results, include a field with a parameters array. If a parameter is a column reference, use {type: "column", value: "column_name"}.
query userFunctionQuery { tri__tri_reporting_form (limit: 10) { tri_facility_id reporting_year tri__getchemname (parameters: [{type: "column", value: "doc_ctrl_num"}]) } }
Standard functions
Standard functions are prefixed with fn__. Use the parameters argument and an optional alias.
Reference: standard functions list (full)
fn__add
Adds the values of any columns and numbers passed in as parameters.
fn__avg
Returns the average of the values of the chosen column. If used alongside other fields, include a
groupByclause.fn__coalesce
Returns the value in the second parameter if the first parameter evaluates to NULL.
fn__coalesceText
Like
fn__coalesce, but returns supplied text when the first parameter is NULL.fn__count
Returns the count of the database field supplied in the first parameter. If used alongside other fields, include
groupBy.fn__dateadd
Adds or subtracts an interval to a date. Date parts include microseconds, milliseconds, second, minute, hour, day, week, month, quarter, year, decade, century, millennium.
fn__datetrunc
Truncates a date to a specified precision (microseconds through millennium). Optional time zone may be supplied (for example,
America/New_York).fn__divide
Divides the values of any columns and numbers passed in as parameters.
fn__extract (fn__datepart is an alias)
Returns a specified part from a date field (microseconds through millennium, including
dowand day-of-year).fn__lpad
Left-pads a string to a specified length using a pad character (defaults to a space).
fn__ltrim
Trims leading characters from a string (defaults to trimming spaces).
fn__lower
Returns the lowercase version of a string field.
fn__max
Aggregate: returns the highest value based on criteria supplied.
fn__min
Aggregate: returns the lowest value based on criteria supplied.
fn__multiply
Multiplies the values of any columns and numbers passed in as parameters.
fn__replace
Returns a modified string by replacing a pattern with replacement text (replacement defaults to empty string).
fn__round
Rounds a numeric field; optional second parameter is decimal places (defaults to 0).
fn__rtrim
Trims trailing characters from a string (defaults to trimming spaces).
fn__stddev
Calculates standard deviation; if used alongside other fields, include
groupBy.fn__substring
Takes a substring starting at the specified index (1 is the start of the field) and length.
fn__subtract
Subtracts the values of any columns and numbers passed in as parameters.
fn__stringagg
Aggregates string values. Optional separator (defaults to space), order-by field, and order direction (ASC/DESC).
fn__sum
Aggregate: sums a numeric field; if used alongside other fields, include
groupBy.fn__trim
Trims leading and trailing characters (defaults to trimming spaces).
fn__upper
Returns the uppercase version of a string field.
fn__variance
Calculates variance; if used alongside other fields, include
groupBy.
Function example
query coalesceField { icis__icis_activity_report (limit: 10) { activity_status_desc fn__coalesce(parameters: ["activity_name", "activity_type_code"], alias: "activity_name") } }
If activity_name is NULL, this returns activity_type_code in its place.
Aggregation functions (Avg, Sum)
Because fn__avg and fn__sum are aggregations, include groupBy when selecting other fields.
query sumField { icis__icis_activity_report (limit: 10, groupBy: [activity_name]) { activity_name fn__sum(parameters: ["total_hours"], alias: "total_hours") } }
Selecting from a function
You can query a function as if it were a table, supplying required parameters.
query functionSelect { icis__air_compliance_monitoring_info (parameters: ["MI00000000000B4127"]) { __all_columns__ } }
Case statements
Use case to enable simple if/else logic when selecting fields.
query caseExample { icis__icis_activity_report (limit: 10) { activity_name activity_type_code state_code (case: { if: {equals: "CA", then: "California"}, elseif: {equals: "TX", then: "Texas"}, else: "Other State" }) } }
Filtering
Apply filters using the where argument on a table.
Multiple filters
query multipleFilters { icis__icis_activity_report ( limit: 10, where: { state_code: {in: ["CT", "RI"]}, activity_type_code: {equals: "INS"} } ) { activity_name activity_type_code state_code } }
OR filters
query orFilter { icis__icis_activity_report ( limit: 10, where: { air_lead_agency_type_desc: {equals: "U.S. EPA"}, or: {air_lcon_code: {equals: "SJV"}} } ) { activity_name activity_type_code air_lead_agency_type_desc air_lcon_code } }
Nested filters
query nestedFilter { icis__icis_facility_interest ( limit: 10, where: { state_code: {equals: "CT"}, or: { city: {equals: "Providence"}, and: {location_address: {like: "%Main%"}} } } ) { facility_name location_address city state_code } }
Reference: available filter operators (full)
When working with string values, most operators are case-insensitive. Where applicable, a case-sensitive variant is available in the format {operator}Sensitive.
beginsWith
- Purpose: Finds values that will start with the supplied value.
- Example:
location_address: {beginsWith: "100"} - Expected Result: All records with addresses that start with 100 will be returned.
- beginsWithSensitive is available for case-sensitive queries.
between
- Purpose: Finds values that are between two values, inclusive of the lower and upper values.
- Example:
total: {between: {lower: 20, upper: 30}} - Expected Result: All records which have a total greater than or equal to 20 and less than or equal to 30 will be returned.
- betweenSensitive is available for case-sensitive queries.
contains
- Purpose: Finds records that have the supplied value anywhere in the field.
- Example:
location_address: {contains: "Main"} - Expected Result: All records that have an address that contains "Main" will be returned.
- containsSensitive is available for case-sensitive queries.
endsWith
- Purpose: Finds values that will end with the supplied value.
- Example:
location_address: {endsWith: "St."} - Expected Result: All records with an address that end with St. will be returned.
- endsWithSensitive is available for case-sensitive queries.
equals
- Purpose: Finds values that will equal the supplied value.
- Example:
state_code: {equals: "CA"} - Expected Result: All records in California will be returned.
- equalsSensitive is available for case-sensitive queries.
excludes
- Purpose: Finds values that will not be like the supplied value anywhere in the field (the opposite of contains).
- Example:
location_address: {excludes: "Main"} - Expected Result: All records where the address does not include Main will be returned.
- excludesSensitive is available for case-sensitive queries.
greaterThan
- Purpose: Finds values that are greater than the supplied value.
- Example:
total: {greaterThan: 30} - Expected Result: All records with a total of 31 or higher will be returned.
- greaterThanSensitive is available for case-sensitive queries.
greaterThanEqual
- Purpose: Finds values that are greater than or equal to the supplied value.
- Example:
total: {greaterThanEqual: 30} - Expected Result: All records with a total of 30 or higher will be returned.
- greaterThanEqualSensitive is available for case-sensitive queries.
in
- Purpose: Finds values that are in the supplied list.
- Example:
state_code: {in: ["MS", "AL", "LA"]} - Expected Result: All records in the states of Mississippi, Alabama, and Louisiana will be returned.
- inSensitive is available for case-sensitive queries.
inSubQuery
- Purpose: Finds values that are in a subquery in the query.
- Example:
state_code: {inSubQuery: "state_query"} - Expected Result: All users whose state is supplied in the subquery aliased as "state_query" will be returned.
- inSensitive is available for case-sensitive queries.
lessThan
- Purpose: Finds values that are less than the supplied value.
- Example:
total: {lessThan: 30} - Expected Result: All records with a total of 29 or lower will be returned.
- lessThanSensitive is available for case-sensitive queries.
lessThanEqual
- Purpose: Finds values that are less than or equal to the supplied value.
- Example:
total: {lessThanEqual: 30} - Expected Result: All records with a total of 30 or lower will be returned.
- lessThanEqualSensitive is available for case-sensitive queries.
like
- Purpose: Finds values that are similar to the supplied value. Uses the % character as a wildcard.
- Example:
location_address: {like: "%Main St."} - Expected Result: All records with any address that begins with Main St. will be returned.
- likeSensitive is available for case-sensitive queries.
notContains
- Purpose: Finds records that do not have the supplied value anywhere in the field.
- Example:
location_address: {notContains: "Main"} - Expected Result: All records that have an address that do not contain "Main" will be returned.
- notContainsSensitive is available for case-sensitive queries.
notBeginsWith
- Purpose: Finds values that will not start with the supplied value.
- Example:
location_address: {notBeginsWith: "100"} - Expected Result: All records with addresses that do not start with 100 will be returned.
- notBeginsWithSensitive is available for case-sensitive queries.
notEndsWith
- Purpose: Finds values that will not end with the supplied value.
- Example:
location_address: {notEndsWith: "St."} - Expected Result: All records with addresses that do not end with St. will be returned.
- notEndsWithSensitive is available for case-sensitive queries.
notEquals
- Purpose: Finds values that are not equal to the supplied value.
- Example:
state_code: {notEquals: "FL"} - Expected Result: All records where the state does not equal Florida will be returned.
- notEqualsSensitive is available for case-sensitive queries.
notIn
- Purpose: Finds values that are not in the supplied list.
- Example:
state_code: {notIn: ["TX", "OK", "KS"]} - Expected Result: All records where the state is not Texas, Oklahoma, and Kansas will be returned.
- notInSensitive is available for case-sensitive queries.
notLike
- Purpose: Finds values that are not similar to the supplied value. Uses the % character as a wildcard.
- Example:
location_address: {notLike: "%Main St."} - Expected Result: All records with users with an any address that do not begin with Main St. will be returned.
- likeSensitive is available for case-sensitive queries.
null
- Purpose: Finds values that are either null or not null.
- Example:
state_code: {null: true} - Expected Result: All records that do not have a value for state_code will be returned.
- Example:
state_abbr: {null: false} - Expected Result: All records that have a value for state will be returned.
regex
- Purpose: Finds values that match the supplied regular expression.
- Example:
location_address: {regex: "(main){1,3}"} - Expected Result: All records that have an address that contains main at least once and at most three times.
- regexSensitive is available for case-sensitive queries.
Casting fields in filters
When you need to cast a field to use a filter operator, include cast in the filter.
query castFilter { icis__icis_activity_report ( limit: 10, where: {planned_begin_date_fy: {greaterThan: 2010, cast: "integer"}} ) { activity_name activity_type_code planned_begin_date_fy } }
Using functions in a filter
You can use lpad, replace, and trim (along with ltrim and rtrim) in filters.
Reference: function attributes supported in filters
lpad
Left-pads a string. Example:
(where: {total: {like: "%1", lpad: [3, "0"]}})replace
Replaces a pattern. Example:
(where: {email: {like: "%.gov%", replace: ["_", "."]}})trim
Trims characters. Example:
(where: {age: {like: "%1", trim: "123"}})ltrim and rtrim
Trim the left or right side of a string, similar to
trim.
Dates
For date fields, use YYYY-MM-DD. For datetime fields, use YYYY-MM-DD HH:MM:SS (24-hour format).
query dateFilter { icis__icis_activity_report ( limit: 10, where: {created_date: {greaterThan: "2021-01-01"}} ) { activity_name activity_type_code created_date } }
Joins
Tables can be joined to each other in queries. Joined tables can also have filters, orderBy, and groupBy applied.
Join example
query joinExample { icis__icis_activity_report (limit: 10, where: {created_date: {greaterThan: "2024-01-01"}}) { activity_name activity_type_code created_date icis__ref_activity_type ( inner_join: {icis__icis_activity_report__activity_type_code: {equals: activity_type_code}} ) { activity_type_desc } } }
Join comparisons to static values
If you need to compare to a static value in a join, append Value to the operator.
query joinValue { icis__icis_activity_report (limit: 10, where: {created_date: {greaterThan: "2024-01-01"}}) { activity_name activity_type_code created_date icis__ref_activity_type ( inner_join: {icis__icis_activity_report__activity_type_code: {equalsValue: "INS"}} ) { activity_type_desc } } }
Reference: join operator types
- cross_join: Cross Join
- full_outer_join: Full Outer Join
- hash_join: Hash Join
- inner_join: Inner Join
- left_join: Left Join
- left_outer_join: Left Outer Join
- right_join: Right Join
- right_outer_join: Right Outer Join
- outer_join: Outer Join
Functions in joins
Joins support functions such as Trim (including LTrim and RTrim), LPad, Replace, Substring, and Cast.
query joinFunction { icis__icis_activity_report (limit: 10, where: {created_date: {greaterThan: "2024-01-01"}}) { activity_name activity_type_code created_date icis__ref_activity_type ( inner_join: { icis__icis_activity_report__activity_type_code: { equals: {activity_type_code: {trim: [" "]}} } } ) { activity_type_desc } } }
Filters in joins
Apply filters to joined tables using a where clause inside the joined table block.
query joinFilter { icis__icis_activity_report (limit: 10) { activity_name activity_type_code created_date icis__ref_activity_type ( inner_join: {icis__icis_activity_report__activity_type_code: {equals: activity_type_code}}, where: {activity_group_code: {equals: "CMM"}} ) { activity_type_desc } } }
Subqueries
DMAP supports a limited version of subqueries. When using insubquery in the primary table, the subquery must have an alias so it can be referenced.
query subqueryExample { rcra__br_reporting( where: {and: {report_cycle: {equalsSensitive: 2019}}, and: {handler_id: {insubquery: "receiverIds"}}} distinct: true ) { handler_id handler_name rcra__br_reporting( subquery: {alias: "receiverIds"} where: { and: {br_form: {equals: "GM"}}, and: {management_location: {equals: "offsite"}}, and: {gen_waste_included_in_nbr: {equals: "y"}}, and: {ship_waste_included_in_nbr: {equals: "y"}}, and: {handler_id: {equals: "AK9690330742"}}, and: {report_cycle: {equalsSensitive: 2019}} } distinct: true ) { receiver_id rcra__rcr_hd_basic( inner_join: {rcra__br_reporting__handler_id: {equals: handler_id}} ) } } }
Pagination
Use limit and offset to paginate through results.
query paging { icis__icis_activity_report (limit: 10, offset: 20) { activity_name activity_status_desc actual_begin_date_fy } }
Ordering results
Order results with orderBy. Valid values include asc, ascNullsFirst, ascNullsLast, desc, descNullsFirst, and descNullsLast.
query orderByExample { icis__icis_activity_report (limit: 10, orderBy: {activity_name: "asc", activity_status_desc: "desc"}) { activity_name activity_status_desc actual_begin_date_fy } }
Ordering with specific sequencing
If your client reorders orderBy fields alphabetically, use a list to enforce sequence.
query orderBySpecify { icis__icis_activity_report (limit: 10, orderBy: [{activity_status_desc: "desc"}, {activity_name: "asc"}]) { activity_name activity_status_desc actual_begin_date_fy } }
Ordering joined columns
To order by a field from a joined table, specify the column using schema__table__column in the primary table’s orderBy.
query joinOrderBy { icis__icis_activity_report ( limit: 10, where: {created_date: {greaterThan: "2024-01-01"}}, orderBy: {activity_name: "asc", icis__ref_activity_type__activity_type_desc: "desc"} ) { activity_name activity_type_code created_date icis__ref_activity_type (inner_join: {icis__icis_activity_report__activity_type_code: {equals: activity_type_code}}) { activity_type_desc } } }
Grouping results
Use groupBy (array of fields) when selecting aggregations alongside other fields.
query groupByExample { icis__icis_activity_report (limit: 10, groupBy: ["activity_name", "activity_status_desc"]) { activity_name activity_status_desc fn__max(parameters: ["activity_status_date"], alias: "activity_status_date") } }
Variables
Variables can be substituted for values in query parameters (for example, limit, filter values, and orderBy). Allowed variable types include String, Int, Float, and OrderBy. String/Int/Float values can also be arrays.
Variables example
Query
query variables($limit: Int!, $offset: Int!, $orderBy: OrderBy!) { icis__icis_activity_report (limit: $limit, offset: $offset, orderBy: $orderBy) { activity_name activity_status_desc activity_status_date } }
Variables
{ "limit": 10, "offset": 30, "orderBy": {"activity_name": "asc", "activity_status_desc": "desc"} }
Filter variables
Query
query filterVariables($state: [String]) { icis__icis_activity_report (limit: 10, where: {state_code: {in: $state}}) { activity_name activity_type_code state_code } }
Variables
{ "state": ["MI", "WI"] }
Export formats
DMAP results can be returned in multiple formats. To export a query’s results, append the format to the URL path.
- CSV:
/query/csv - Excel:
/query/excel - XML:
/query/xml - JSON:
/query/json - JSONP:
/query/jsonp?callback=callback-value - Parquet:
/query/parquet - HTML:
/query/html - PDF:
/query/pdf - GraphQL:
/query/graphql
The GraphQL export format is similar to the standard response (/query) but does not nest results from joined tables. This can improve compatibility with some GraphQL clients.
Limitations
The API has a maximum record limit of 100,000,000. There is also a hard cutoff of 15 minutes for a query; any query that exceeds that limit will not return results. If you expect large result sets, use pagination to page through results.
This API is not a true GraphQL implementation. It does not support mutation, query fragments, introspection, or a schema file. It provides a GraphQL-compliant syntax to perform complex queries that are not possible within the Envirofacts REST service.
Related Envirofacts API tools
- Data & Developer Services
Hub page for Envirofacts developer resources, documentation, metadata tools, and update schedules. - Envirofacts Web Services
Central hub for Envirofacts APIs, including Envirofax Data Service API, DMAP GraphQL API, and the UV Index API. - Envirofax Data Service API
REST endpoints for programmatic access to Envirofacts data using the Envirofax service family. - Envirofacts REST API Viewer
Interactive tool to explore and test REST API calls. - API statistics (counts by year, month, and program)
Usage statistics for Envirofacts APIs.
Help and feedback
For DMAP GraphQL API usage questions or suggestions, please contact the Envirofacts team.
