Flies and Schools
Basics

Photo Credit: University of Florida
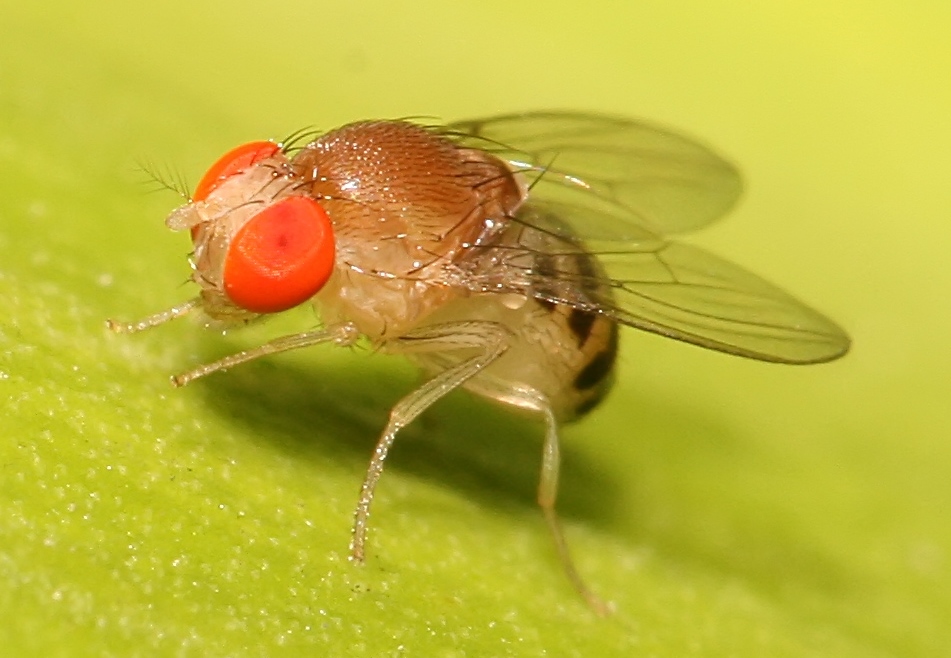

Fruit Fly - Drosophila sp.
Photo Credit: University of Minnesota
There are thousands of species of flies, of which only a few are common pests. These are generally known by their common name:
- House fly.
- Stable fly (also known as biting fly).
- Face fly.
- Garbage fly.
The common element among these pests is the need to breed in animal waste and decaying organic material; some even feed on mammal blood.
Life Cycle: Flies undergo a complete metamorphosis (or change) throughout their life cycles. Female flies deposit their eggs, often numbering over 100, in animal waste or moist organic material, where the eggs hatch and become larvae or “maggots."
From this stage the larvae develop into pupa, which have a hardened shell. The adult fly develops within this hardened shell. This transformation occurs in a little as seven days in the summer, with ideal temperature.
Health Concerns
Flies are carriers and transmitters of numerous diseases as a result of breeding and feeding on animal waste, garbage, and human foods. Flies are most known for carrying bacterial and viruses that cause:
- Diarrhea.
- Cholera.
- Food poisoning.
- Yaws.
- Dysentery.
- Eye infections.
Integrated Pest Management (IPM) Strategies
While adult flies are the most bothersome, the point of greatest IPM control is often the larval stage. By eliminating the habitat preferred by larvae, the fly population can be better managed. This includes removing:
- Animal waste.
- Garbage.
- Decaying plant matter.
- Moist environments for egg deposition.
Chemical pesticides are ineffective in the long-term. Flies are able to develop resistance to pesticides due to their rapid life cycle. Use of increased air movement and screens in areas frequented by people can be effective.
Fly traps and repellents have varying effects, dependent upon the species and method of attraction. Their use should not be considered an alternative to the suggestions listed above. Always read the label thoroughly before using fly traps or repellents.
For More Information
- University of Illinois IPM for Flies in School
- University of California's IPM Online page - Pests of Homes, Structures, People and Pets: Flies
- Read more about integrated pest management.
