Growing DASEES: EPA Tool Helps Cultivate Better Decisions
A vacant lot in the heart of a neighborhood poses both an opportunity and a challenge – for example, the community could transform it into a park to increase green space, or they could build affordable housing to meet growing demands. How should they decide which effort to pursue?
Any option for revitalizing a vacant lot comes with a host of decision factors to consider such as zoning laws or other regulations, relevant government entities, potential resulting economic benefits, how the development may affect residents and any resulting environmental effects. Additionally, the residents, businesses, local government, and others may have different ideas for the space. So how can a community factor in all of this when deciding what best meets their needs and provides the most benefits?
An EPA tool, Decision Analysis for a Sustainable Environment, Economy, and Society, or DASEES, is designed to help address these kinds of complicated decision-making needs.
“Decision analysis has been described as “a formalization of common sense for decision problems which are too complex for informal use of common sense,” said EPA environmental engineer Brian Dyson, one of the founding designers of the tool. “It pulls multiple pieces of information together to allow people to evaluate the pros & cons or tradeoffs of implementing different options.”
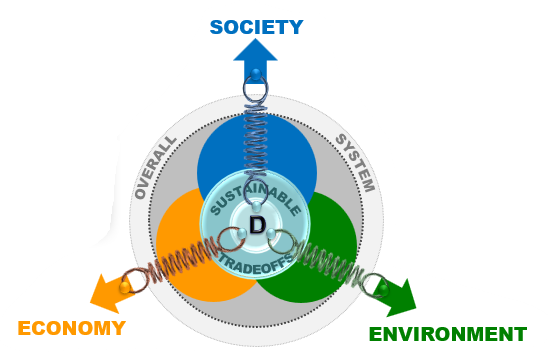
“DASEES allows you to capture the decision process in a clear and understandable manner, allowing people to see how information is used to evaluate options,” added Tim Canfield, EPA research ecologist/limnologist and DASEES co-creator.
The decision process, often termed structured decision making, walks tool users through the steps of identifying the problem and the decision context, defining the desired outcomes and performance measures, identifying options for achieving those outcomes, evaluation of options, and finally, deciding on an option and taking action. DASEES recognizes there may be multiple objectives impacting decisions and provides a process to gain clarity on potential tradeoffs as options for sustainable outcomes are assessed.
DASEES can be used for problems or decisions of any size or scope, from selecting a preferred vehicle to purchase to coordinating flood planning in multiple, interconnected regions.
“DASEES helps identify where you should put your efforts and limited resources to better inform your decisions,” said Canfield.
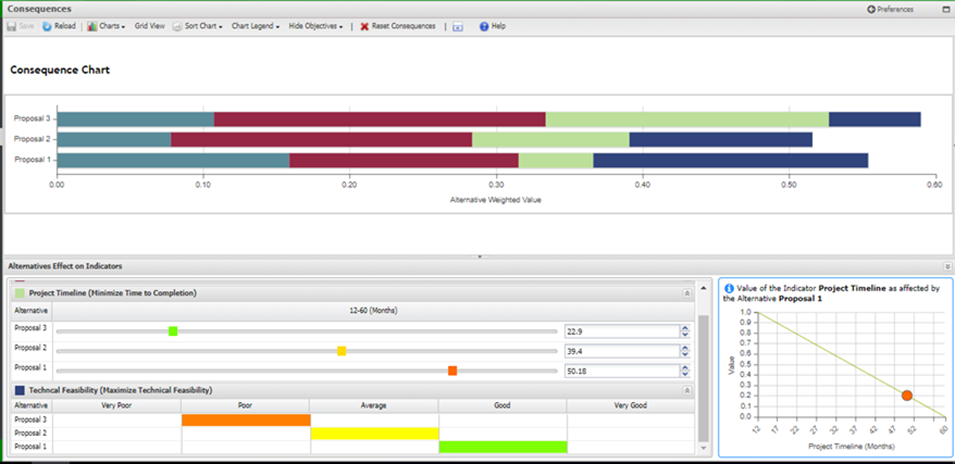
The tool supports EPA’s efforts towards cooperative federalism, facilitating interactions among regions, states, Tribes, and communities working together to solve a common problem. It helps all parties focus in on a shared understanding of the issue at hand to bring in the right technical people, models, data or resources to make decisions to address the problem.
DASEES has been used for addressing non-point source pollution in Puerto Rico, planning for natural disaster mitigation in Florida and Louisiana, and prioritizing contaminated site cleanup in Idaho. DASEES is currently being used by the Chickasaw Nation to support drinking water and wastewater infrastructure upgrades for communities in the Chickasaw Nation.
“The Chickasaw Nation is using the DASEES tool to focus on its highest priority community needs in water and wastewater infrastructure and the projects have an opportunity to make a generational change within the Chickasaw Nation Reservation,” said Kristopher Patton, Chickasaw Nation’s Director of Natural Resources.
The tool is freely available to all users as a downloadable application, available on EPA’s website here.
