Drinking Water Optimization Program
The Area-Wide Optimization Program (AWOP) provides technical assistance via tools and approaches designed to help drinking water systems meet water quality optimization goals and provide an increased – and sustainable – level of public health protection to their consumers. The program focuses on enhancing existing treatment and operations, which generally leads to improved operations at drinking water systems. For some systems (e.g., especially those with inadequate or aging water infrastructure) the program approach may identify needed capital improvements. Other systems may be able to meet optimization goals with their existing treatment and infrastructure.
Adoption of the program’s monitoring and water quality goals and the application of the program approach can help improve drinking water compliance, as well as increase consumers’ confidence in their drinking water. The optimization goals are more stringent than EPA’s regulatory requirements and program participation is voluntary. Many states currently participate in multi-state optimization programs, which are organized by EPA Region(s), and the participating states often use recognition programs to highlight water systems that have met program goals. Historically, the program has involved the development of technical assistance approaches within drinking water primacy agencies (typically states), through training by EPA, which the states can then apply to their public water systems. However, EPA is now working to increase the program’s impact by engaging third-party technical assistance providers in the training offered by the Agency and the application of these tools to water systems.
Approach
EPA designed AWOP to enhance public health protection by optimizing the performance of public water systems. A successful AWOP includes three key components:
- Status - Enhanced surveillance of PWS performance, which helps determine the relative need of the water systems (based on water quality and anticipated public health risk) and target assistance to those most in need.
- Targeted Performance Improvement - Targeting activities for improving drinking water quality to “optimum” levels that go beyond regulatory requirements; this training helps transfer water treatment skills to water system operators and sustain improvements in drinking water quality.
- Maintenance - Ongoing improvement to sustain and enhance the program through collaboration with partners in the AWOP network and integration of optimization approaches into related drinking water programs (e.g., capacity development).
Benefits
Participants in Area-Wide Optimization Program (AWOP) have cited multiple benefits including:
Enhanced State Staff, TA-Provider Staff, and Water-System Staff Capability and Motivation
- Training is provided to participants on optimization tools and approaches, which are demonstrated at drinking water systems as field-proven practical and implementable approaches to improving water quality.
- Water system staff gain increased technical understanding, as well as priority-setting and problem-solving skills.
- Relationships among participants (e.g., state compliance assistance staff, third-party TA providers, and the regulated water system community) are developed and enhanced.
Compliance Assistance for Small and Large Water Systems
- Provides a cost-effective compliance assistance/improvement approach. An example of this type of impact is shown below.
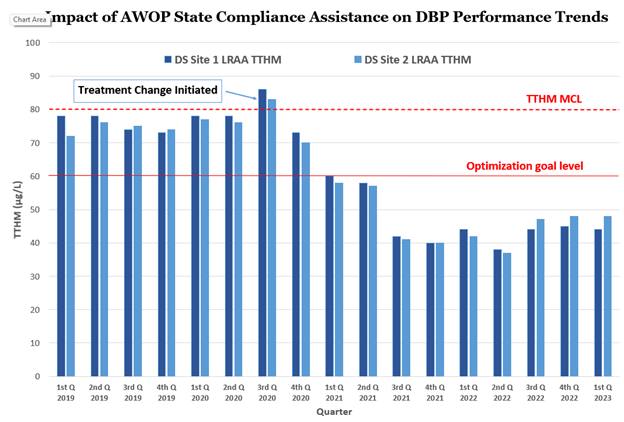
Demonstration of the impact of optimization based technical assistance activities on disinfection byproduct (DBP) levels in the distribution system are shown over a four-year period. Total trihalomethane (TTHM) levels are plotted on the y-axis for each quarter. The TTHM values decreased after a state provided technical assistance to this water system. The optimization based technical assistance activities that the primacy agency provided prior to the treatment change included an assessment of disinfection byproduct formation in the water plant, a DBP formation potential study and jar testing to evaluate the potential for additional organics removal. This latter activity indicated the potential for a treatment change which ultimately resulted in reduced TTHM levels at their distribution system monitoring locations. The graph shows that the locational running annual averages (LRAAs) for TTHMs leading up to the treatment change were very close to being out of compliance (with the TTHM maximum contaminant level, MCL, equal to 80 µg/L). However, once this change was made the system was able to both comply with the TTHM requirements and meet the optimization goal level. Though not shown, this change also resulted in lower formation of haloacetic acids (HAA5) in this system – as well as overall lower DBP formation in their consecutive system.
Effective Use of State Resources
- Resources allocated to systems based upon numerous factors, such as greatest need for water quality improvements and historical compliance violation vulnerability.
- The correct technical assistance tools can be targeted for each system.
Improved Treatment Plant Performance and Distribution System Operations
- Represents a long-term, sustainable, approach.
- Fosters the enhanced capability of water system operators.
- Documents the data-based, results-driven program.
- Demonstrates improvement using plant-performance and water-quality trends.
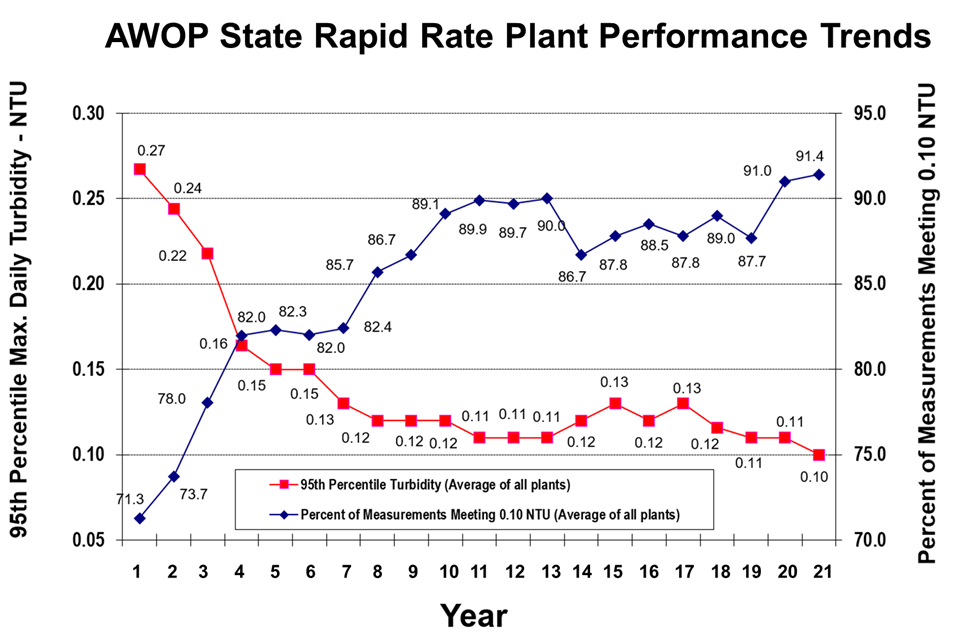
Average turbidity performance data from all of the rapid rate surface water treatment plants from an AWOP state. On the primary y-axis the maximum daily turbidity is plotted in units of NTU; on the secondary y-axis the percent of measurements meeting 0.1 NTU, which is the filtered water turbidity performance goal for this state. These data are shown over a 21-year period. Throughout this time the average maximum turbidity consistently decreased (starting at 0.27 NTU and dropping to 0.10 NTU). Additionally, the percent of the measurements meeting the AWOP goal consistently increased from 71.3 to 91.4%.
Become Involved
States and third-party TA providers can both participate in AWOP, with the TA providers helping participating states leverage their compliance assistance resources. Parent EPA Regions generally participate when one or more of their respective states are involved. For more information contact:
Current Program Participants
The Area-Wide Optimization Program (AWOP) is a unique partnership that fosters the continued growth of the program. Current program participants include:
- EPA Office of Ground Water and Drinking Water (OGWDW), Standards and Risk Management Division, Technical Support Branch (TSB) Cincinnati, OH: leads the development and implementation of AWOP activities nation-wide and helps sustain the network of participating states and water systems.
- OGWDW Drinking Water Capacity and Compliance Assistance Division (Washington, DC): supports the integration of AWOP into Capacity Development, Technical Assistance (TA) programs, and regulatory implementation and compliance strategies.
- EPA Regions: multiple EPA Regions use AWOP to support direct implementation responsibilities, sustain the AWOP by facilitating state implementation, and support the development of new optimization approaches.
- Association of State Drinking Water Administrators (ASDWA): supports and advocates the implementation of AWOP within existing and potential state drinking water programs.
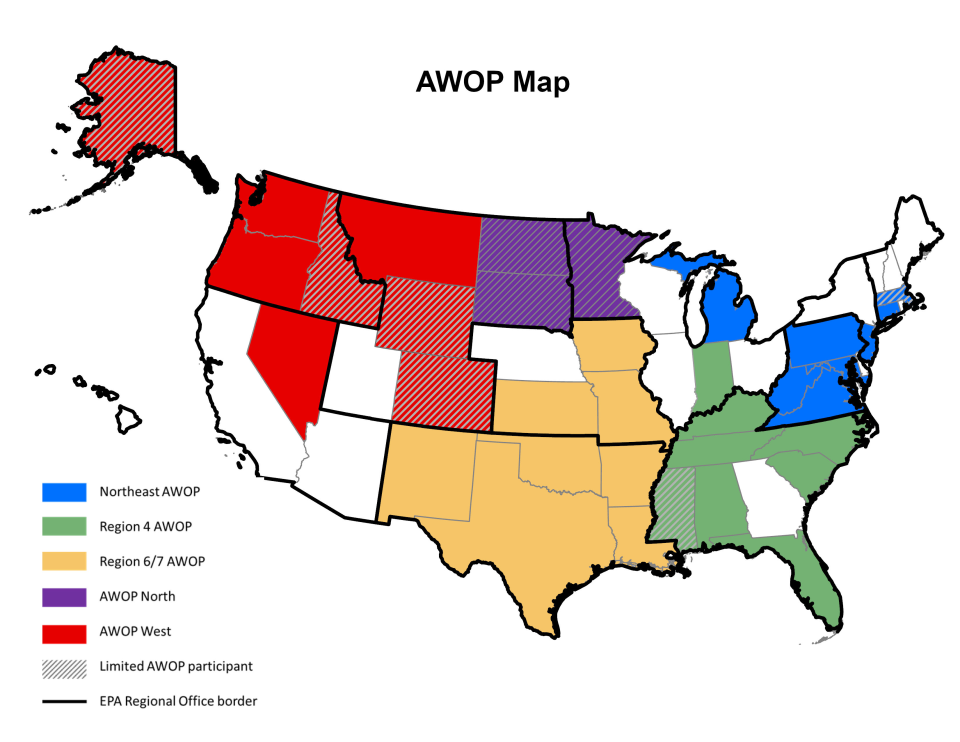
- State participation (as of June 2025) is depicted in the map that follows:
Related Information
- Association of State Drinking Water Administrators (ASDWA) AWOP page - additional information on the Area-Wide Optimization Program (AWOP).
- Handbook: Optimizing Water Treatment Plant Performance Using the Composite Correction Program (pdf) (2.6 MB) - resource document for optimizing the performance of existing surface water treatment facilities to provide protection from microbial contamination.
- Drinking Water Instrumentation Data Integrity Checklists (pdf) - intends to serve as a resource to ensure the accuracy and reliability (i.e., the “integrity”) of data generated using various instruments that measure water quality parameters.
- Generating High-Quality Turbidity Data in Drinking Water Treatment Plants to Support System Optimization and Monitoring document
- Optimization Tools for Reducing Disinfection Byproducts - includes a four-part recorded webinar series introducing tools that water systems can use as well as several study protocols and supporting spreadsheets.
- Tools and approaches for collecting water samples:
- Implementing AWOPs through the Capacity Development and Drinking Water State Revolving Fund Programs (pdf) (475 K)
- Partnership for Safe Water – a program that provides the framework for drinking water utilities to optimize their water plant and distribution system operations, through a self-assessment process, to meet specific water quality and operational goals.
