Grand Calumet River AOC
Caitie Nigrelli
(nigrelli.caitlin@epa.gov)
312-886-1430
On this page:
Overview
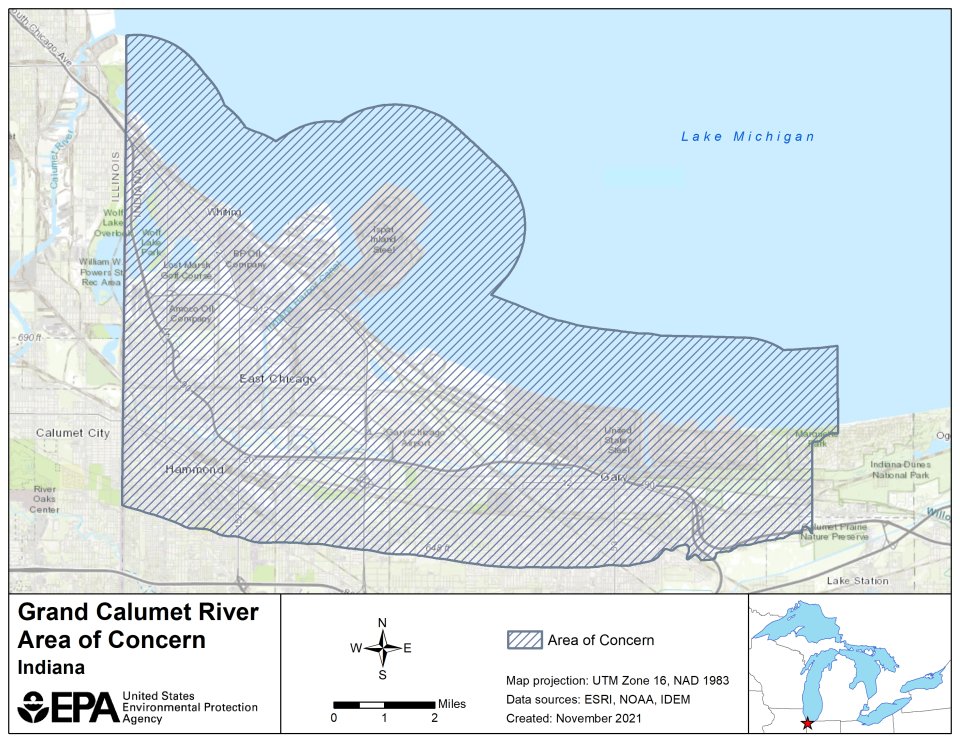
The Grand Calumet River is in one of the most heavily industrialized areas in the United States, flowing mainly through northwestern Indiana. Beginning in the 20th century the area began experiencing an influx of steel mills, foundries, chemical plants, oil refineries, meat packing industries, and pharmaceutical industries. Prior to the 1972 Clean Water Act, industries released industrial waste and some nearby cities discharged untreated sewage into the river. In addition, potential nonpoint sources of contaminants, such as industrial and urban runoff may have affected water quality in the river.
The river was designated as an Area of Concern (AOC) under the Great Lakes Water Quality Agreement of 1987, largely due to legacy pollutants. These pollutants remain in the environment for extended periods of time after they are introduced and were found in sediments at the bottom of the Grand Calumet River, Indiana Harbor and Ship Canal. These legacy pollutants include:
- Polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs)
- Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs)
- Heavy metals including but not limited to mercury, cadmium, chromium, and lead
- Oil and grease
Beneficial Use Impairments
The Grand Calumet River has all 14 Beneficial Use Impairments (BUIs). BUIs are designations created by the International Joint Commission that identify some of the most severe examples of environmental degradation. When restoration or cleanup projects begin to make progress, monitoring of the site will eventually show sufficient improvement in environmental health. Once a BUI reaches this point, it can be “removed”, or the beneficial use is restored. When all BUIs have been removed, EPA and the state of Indiana can begin the process of delisting.
- Restrictions on Fish and Wildlife Consumption
- Eutrophication or Undesirable Algae
- Tainting of Fish and Wildlife Flavor
- Restrictions on Drinking Water Consumption or Taste and Odor Problems (PDF) - Removed March 2012
- Degradation of Fish and Wildlife Populations
- Beach Closings
- Fish Tumors or Other Deformities
- Degradation of Aesthetics
- Bird or Animal Deformities or Reproduction Problems
- Added Costs to Agriculture or Industry (PDF) - Removed September 2011
- Degradation of Benthos
- Degradation of Phytoplankton and Zooplankton Populations
- Restrictions on Dredging Activities
- Loss of Fish and Wildlife Habitat
Remediation and Restoration Work
In order to delist the Grand Calumet River AOC, EPA and partners identified 12 sediment remediation and five habitat restoration projects or management actions. The goal of sediment remediation is to address sediments contaminated severely with PCBs, PAHs, and heavy metals. Sediment may be addressed by dredging and/or capping to prevent further release of contaminants.
Habitat in the AOC had lost functionality due to urbanization and habitat destruction. Over 1,000 acres of habitat in the AOC will be restored, including globally rare dune and swale habitat. To delist this AOC, partners must meet habitat-related BUI removal criteria (PDF). Restoration and cleanup at this AOC will improve one of the most heavily polluted areas in the Great Lakes watershed and allow the surrounding communities to benefit more fully from the river and surrounding ecosystems.
- Documents on Restoring the Grand Calumet River AOC
- View Remediation and Restoration Projects for this AOC
-
Remediation Project Highlight
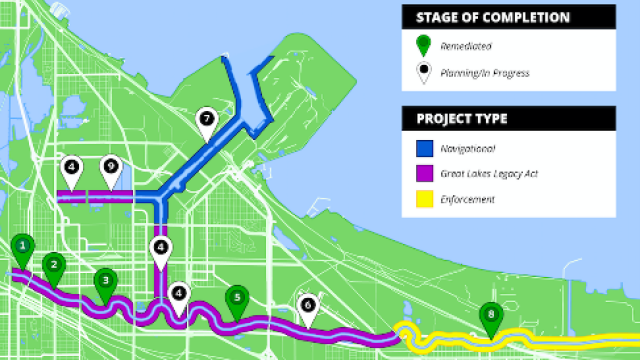
Remediate nearly 190,000 cubic yards of contaminated sediment through dredging and capping, preventing contaminants from entering the food chain.
-
Restoration Project Highlight

Restore globally rare dune and swale habitat and riverine wetlands through the control of woody and herbaceous invasive species.
Partners
- U.S. Army Corps of Engineers - Chicago District
- U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service
- Citizen's Advisory for the Remediation of the Environment Committee
- East Chicago Waterway Management District
- Indiana Department of Environmental Management
- Indiana Department of Natural Resources
- Atlantic Richfield - British Petroleum
- Grand Calumet River Restoration Fund Council
- Lake County Parks and Recreation Department
- Northern Indiana Public Service Company