EPA's Technical Support Centers
EPA has five Technical Support Centers (TSCs) that offer scientific and engineering expertise to contaminated site decision makers within EPA, including remedial project managers and on-scene coordinators.
EPA’s Regional Offices network with the states and tribes within their area to request assistance. These centers, located around the country, help to integrate science and technology into hazardous waste clean-up activities.
Areas of technical support include site characterization, modeling, monitoring, assessment, and remediation technologies. The TSCs advance the use of state-of-the-science information and help ensure coordination and consistency in the application of remedial technologies. The TSCs are actively providing support at many of EPA’s most complex and high-priority cleanup sites, helping to accelerate cleanup operations and advance economic revitalization.
Superfund and Technology Liaisons (STLs) are EPA scientists and engineers who are important links between regional staff and the TSCs. STLs in each region work with remedial project managers, corrective action staff, and on-scene coordinators to identify available resources and specialized expertise to assist with specific clean-up sites, tasks, or projects.
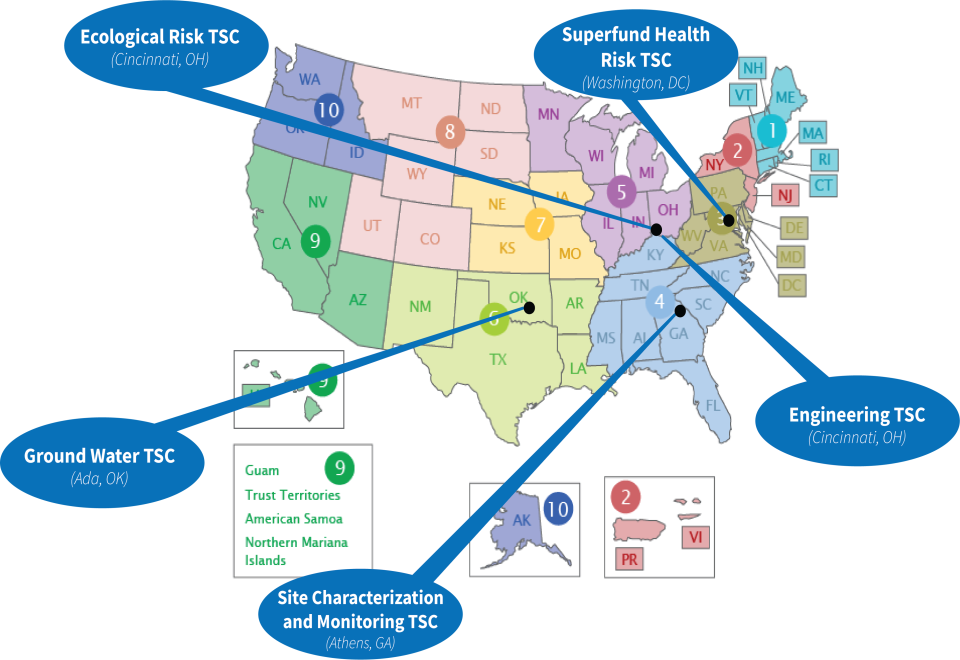
EPA Technical Support Centers
Engineering Technical Support Center
Director: David Gwisdalla (gwisdalla.david@epa.gov)
Provides short- and long-term assistance to Superfund and RCRA Corrective Action staff. Assistance focuses on treatment technologies and engineering approaches to site management at any phase from problem identification through remedial action.
Ground Water Technical Support Center
Acting Director: Stephanie Ross (ross.stephanieD@epa.gov)
Provides support to EPA staff on issues regarding subsurface contamination, contaminant fluxes to other environmental media (e.g., surface water or air), and ecosystem restoration. The Center creates critical links between research and real-world problems, providing a testing ground for research and allowing scientists to focus on high priority problems.
Site Characterization and Modeling Technical Support Center
Acting Director: David Gwisdalla (gwisdalla.david@epa.gov)
Provides technical assistance on complex hazardous waste site characterization issues through specialized teams of scientists equipped to aid the regions with screening and site characterization. The diversity of expertise available through allows the Center to work with the regional programs at any time during a site characterization event.
Superfund Health Risk Technical Support Center
Directors: Dahnish Shams (shams.dahnish@epa.gov) and Nicholas Barnett (barnett.nicholas@epa.gov)
Provides site-specific guidance and expertise for preparing human health risk assessments on the types of hazardous waste sites addressed by EPA land cleanup programs.
Ecological Risk Assessment Technical Support Center
Acting Director: Kelly Dipolt (dipolt.kelly@epa.gov)
Provides technical information and addresses scientific questions on topics relevant to ecological risk assessment at hazardous waste sites for Superfund and RCRA Corrective Action staff. Center experts develop state-of-the science responses for ecological risk assessments. Serves as a central communication point distributing responses to interested parties outside the Agency.
