Clean Water Indian Set-Aside (CWISA) Program
EPA’s Pacific Southwest (Region 9) implements and enforces federal environmental laws in Arizona, California, Hawaii, Nevada, the Pacific Islands, and 148 Tribal Nations.
- Purpose
- How to Apply
- Funding History
- Eligible Activities
- Eligibility Requirements
- Additional Resources
- Contacts
- Documents
Purpose
To assist federally recognized Tribes within EPA Region 9 to improve wastewater infrastructure. Funds may be used for planning, design and construction of wastewater collection and treatment systems.
How to Apply
To apply for funding from the CWISA Program, Tribes must first contact their Indian Health Service (IHS) Area Office to determine if their wastewater needs are eligible to be entered into the IHS Sanitation Deficiency System (SDS). The SDS is an inventory of projects developed to address existing sanitation deficiencies in American Indian and Alaska Native communities. Projects that support future growth are not included. EPA uses the SDS, in coordination with the IHS, to identify and select priority wastewater projects for funding. Projects are prioritized in the SDS based on eight factors: health impact, existing deficiency level, previous service, capital cost, operation and maintenance capability, Tribal contributions, local tribal priority, and local conditions. For example, projects that resolve public health concerns rank higher than projects designed to rectify water quality problems.
EPA awards funds annually. Tribes have an option of receiving a direct grant or coordinating an Interagency Agreement (IA) with their corresponding IHS area office. When a project is selected for funding, EPA contacts the Tribe and requires a written response endorsing the project and electing a funding mechanism before processing the award.
| Year 1 | January–May : Tribes identify sanitation needs to IHS Area Offices June: Deadline for submission of Tribal needs to IHS Areas June–July: IHS Areas review and rank projects submitted to the SDS August–October: IHS HQ reviews IHS Area SDS project submissions November: Final SDS lists made available to EPA CWISA Program |
|---|---|
| Year 2 | December–March: EPA Regional CWISA Programs select projects from SDS April–September: EPA Regional CWISA Programs notify Tribes of selected projects and award CWISA Program funds |
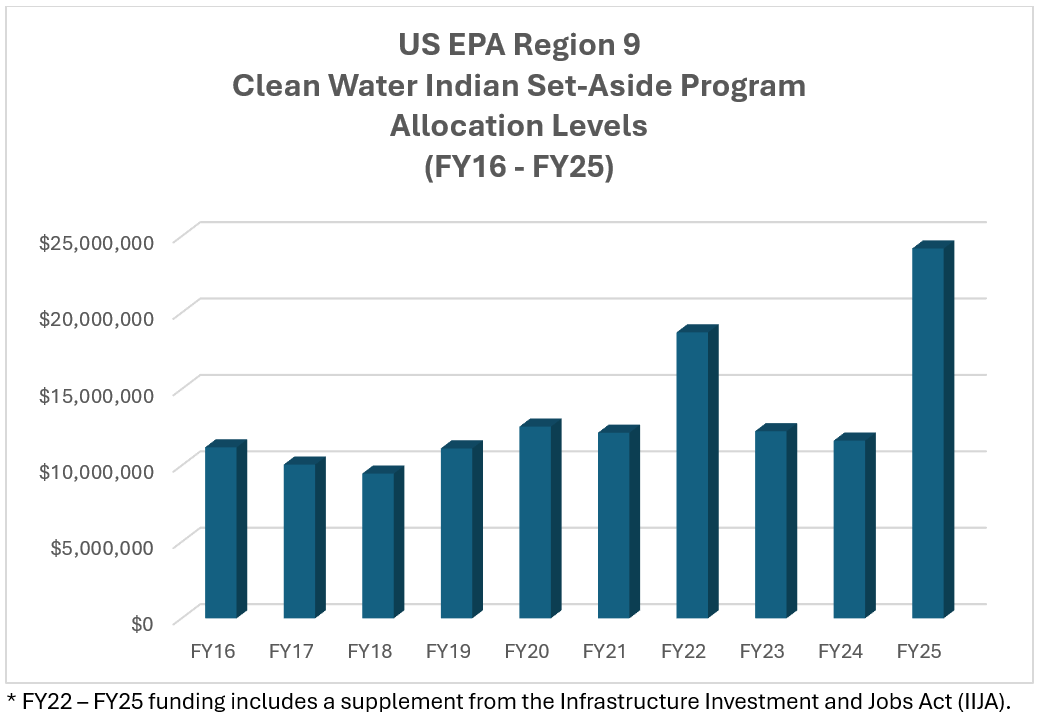
Funding History
The Clean Water Act authorized CWISA Program funding via one-half of one percent (0.5 percent) from the Construction Grants Program appropriations for fiscal years 1987 through 1990. In 1992, Congress gave EPA the authority to take a 0.5 percent set-aside from the Clean Water Act Title VI (Clean Water State Revolving Fund) appropriation following the phase-out of the Construction Grants Program. Beginning with EPA's FY 2001 Appropriation's Bill, Congress authorized an increase from 0.5 percent to 1.5 percent of the Clean Water State Revolving Fund's (CWSRF) appropriation for the CWISA Program. In FY 2010, Congress authorized an increase from 1.5 percent to 2 percent from the CWSRF for the CWISA Program. Since FY 2016, the CWISA appropriation from Congress has been either 2 percent of the CWSRF or $30 million, whichever is greater.
The amount of CWISA funding available to an EPA region is based on its proportion of Tribal wastewater needs, as identified in the IHS SDS database. The SDS is updated on an ongoing basis to account for inflation and changing state and federal standards; to add new deficiencies; and to remove deficiencies that have been addressed by projects funded by IHS and other entities such as EPA.
Eligible Activities
All projects funded by the CWISA Program must support wastewater-related activities or projects. CWISA Program funds cannot be used to pay for the cost of operation and maintenance of the wastewater facility, nor can they be used to pay for repairs to the treatment system in emergency situations. Project components eligible for funding include:
- Project planning, design, and Preliminary Engineering Report (PER)
- Infrastructure construction and major sewer rehabilitation
- Wastewater treatment facilities (conventional or alternative)
- Correction of combined sewer overflows
- Collector sewer pipelines
- On-site wastewater treatment systems (e.g., septic systems)
- Follow-up and as-built drawings of funded wastewater projects
- Operator training on new infrastructure equipment for first year
Eligibility Requirements
CWISA Program funds can only be used for projects that will increase a Tribe’s access to wastewater sanitation, and these projects must be listed in the IHS SDS database. Any Indian Tribe, band, group, or community recognized by the Bureau of Indian Affairs (BIA) in its list of all federally recognized Tribes in the United States is eligible for funding through the CWISA program, unless they have been deemed ineligible to receive federal funds by another agency or department of the federal government.
Additional Resources
EPA can also assist Tribes to develop infrastructure projects and coordinate with the IHS. EPA-directed contract support can be used to assist a Tribe to develop a preliminary engineering report (PER) and other supporting documents. Similarly, EPA’s Water Technical Assistance (WaterTA) program can help Tribes to understand their wastewater infrastructure needs and plan for the future. To further discuss these resources, please reach out to the appropriate Tribal Water Infrastructure Project Officer.
The National CWISA Program Site includes links to the national CWISA program guidance, FAQs and recent regional funding allotments.
Documents
Free viewers and readers are available to access documents on our website. If you encounter issues with assistive technology, please contact us.
-
Fact Sheet: EPA Region 9 Clean Water Indian Set-Aside Program (pdf)
(600.26 KB, October 2025)
EPA Pacific Southwest (Region 9) fact sheet with information about EPA's Clean Water Indian Set-Aside (CWISA) Program, which provides annual funding for federally recognized Tribes within Region 9 for wastewater infrastructure improvements.
Related Resources
- Clean Water Emerging Contaminant (EC) Program
- National Program for Tribal Wastewater Infrastructure Funding
- Closing America’s Wastewater Access Gap
- Water Technical Assistance (WaterTA)
- Drinking Water Tribal Set-Aside (DWTSA)
- Drinking Water Emerging Contaminant Programs
- Lead Service Line Replacement (LSLR) Program
- PFAS Drinking Water Sampling Project
- School Drinking Water Lead Testing Project
Contacts
To apply for funding from the CWISA Program, Tribes must first contact their IHS Area Office to determine if their wastewater needs are eligible to be entered into the IHS Sanitation Deficiency System (SDS).
For general information about the CWISA Program, please contact:
Nancy Sockabasin
sockabasin.nancy@epa.gov
(415) 972-3772
To discuss a specific wastewater infrastructure project, please contact your Infrastructure Project Officer. Geographic assignments are aligned with Indian Health Service Offices within Region 9.
Western Arizona District and Sacramento and Ukiah Field Offices
Sara McGillewie, Project Officer
mcgillewie.sara@epa.gov
(213) 244-1859
Navajo Nation Area
Adam Ramos, Project Officer
ramos.adam@epa.gov
(415) 972-3450
Tucson Area
Nancy Sockabasin, Project Officer
sockabasin.nancy@epa.gov
(415) 972-3772
Escondido District and Clovis Field Office
Madeleine Tango, Project Officer
tango.madeleine@epa.gov
(619) 874-0568
Reno District
Katie Velazquez, Project Officer
velazquez.katie@epa.gov
(213) 244-1834
Eastern Arizona District and Redding District
Emma Young, Project Officer
young.emma@epa.gov
415) 594-7698
