Biointermediates
- About Biointermediates
- Biointermediates Compliance Workshop 2022
- Registration, Reporting, Recordkeeping, and Attest Engagements
- Improperly Produced Biointermediates
About Biointermediates
To promote efficiency and opportunity in producing renewable fuels, the Renewable Fuel Standard (RFS) program includes a regulatory framework for biointermediates. Biointermediates are feedstocks that have been partially converted at one facility but are then sent to a separate facility for their final processing into a renewable fuel.
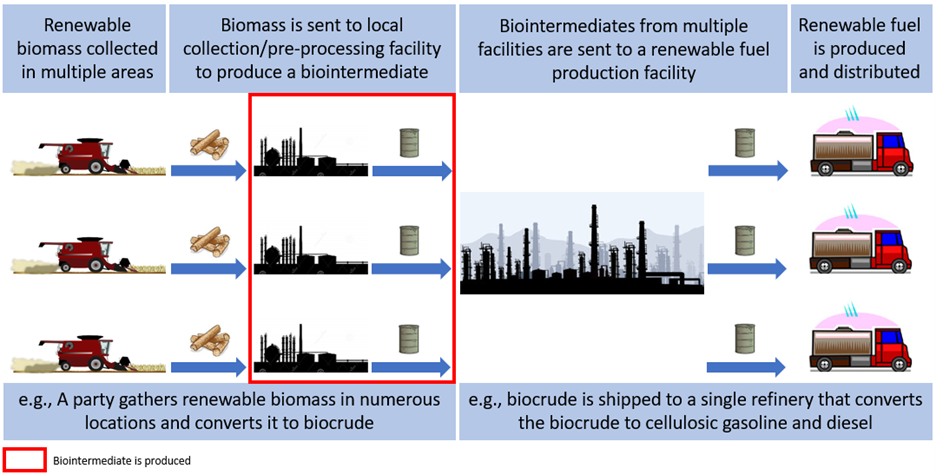
Only the following are allowed to be used as biointermediates as defined in 40 CFR section 80.2:
- Biocrude
- Biodiesel distillate bottoms
- Biomass-based sugars
- Digestate
- Free fatty acid (FFA) feedstock
- Glycerin
- Soapstock
- Undenatured ethanol
Producers who are interested in a potential biointermediate not listed should contact the Fuels Program Support Helpdesk at FuelsProgramSupport@epa.gov.
Learn more:
Biointermediates Compliance Workshop 2022
EPA conducted an RFS biointermediates implementation workshop on September 29, 2022. To see details of the workshop including presentation slides, see Workshop Biointermediates Compliance 2022.
Registration, Reporting, Recordkeeping, and Attest Engagements
The 2020-2022 Renewable Volume Obligation (RVO) rule outlined specific registration, reporting, recordkeeping, and attest engagement requirements for biointermediate producers that participate in the RFS program. Information about these requirements is below.
Registration for Biointermediates
Facilities must be registered to produce biointermediates or renewable fuels produced from biointermediates.
For information of the steps involved in registration, see:
- Job Aids for Biointermediates Registration
- How to Update Existing Companies, Facilities, and Users for Part 80 Fuels Program
Reporting for Biointermediates
Biointermediate producers and renewable fuel producers who use biointermediates to produce renewable fuel have reporting requirements under the RFS program. These reporting requirements include quarterly and annual compliance reporting, as well as Renewable Identification Number (RIN) transaction reports (renewable fuel producers only).
- EMTS Transaction Report - Download and submit within EMTS
For information on the quarterly and annual reports for renewable fuel producers, see List of Quarterly and Annual Reports for Renewable Fuel Standard.
Recordkeeping for Biointermediates
Biointermediate producers, renewable fuel producers who use biointermediates to produce renewable fuel, and biointermediate importers must generate and use product transfer documents and keep records to comply with the RFS program. Third parties who submit reports or perform services, such as attest auditors, Quality Assurance Plan (QAP) providers, and professional engineers performing engineering reviews, also must generate and keep records.
- 40 CFR section 80.1453 - product transfer documents
- 40 CFR section 80.1454 - recordkeeping
Attest Engagements for Biointermediates
Annual attest engagements are required for biointermediate producers and renewable fuel producers who use biointermediates to produce renewable fuel. Attest engagements are performed as a check on records and compliance reports by a third-party attest auditor who is a certified public accountant (CPA) or certified internal auditor (CIA). These annual attest engagements are performed for the party by the attest auditor. The annual attest engagement report is submitted to EPA by the attest auditor by June 1, for the preceding compliance period.
- How to Submit Attest Engagement Reports
- 40 CFR section 80.1464 - attest engagements
Improperly Produced Biointermediates
Improperly produced biointermediates are biointermediates that have been identified by an independent third-party auditor under 40 CFR section 80.1477(d) as not having been produced consistent with applicable RFS requirements. The use of improperly produced biointermediates to produce renewable fuel and generate RINs results in potentially invalid RINs (PIRs). Independent third-party auditors are required to notify EPA, the biointermediate producer, and the affected renewable fuel producer after the auditor has identified an improperly produced biointermediate. Any resultant PIRs must undergo the PIR process under 40 CFR section 80.1474 to remediate the PIRs.
Independent auditors are required to notify EPA by contacting the Fuels Program Support Helpdesk at FuelsProgramSupport@epa.gov.
