EPA EcoBox Tools by Effects - Effects In ERA
Planning and Problem Formulation Phase: Identifying Potential Ecological Effects
According to U.S. EPA’s Guidelines for Ecological Risk Assessment (1998), problem formulation is a process for generating and evaluating preliminary hypotheses about why ecological effects have occurred—or may occur—from human activities. The process of problem formulation offers a systematic approach for organizing and evaluating available information on stressorsAny physical, chemical, or biological entity that can induce an adverse response (synonymous with agent). and possible effects. During this process, the following questions related to ecological effects might be considered.
- What are the type and extent of available ecological effects information (e.g., field surveys, laboratory tests, or structure-activity relationships)?
- Given the nature of the stressor(s) (if known), which effects are expected to be elicited by the stressor(s)?
- Under what circumstances will effects occur?
A plan for analyzing and characterizing ecological risks is determined based on the integration of available information on sources, stressors, effects, and ecosystem and receptor characteristics.
Analysis Phase: Characterizing Effects
During the analysis phase—which comprises exposure assessment and effects assessment—ecological effects are characterized. As described in U.S. EPA’s Guidelines for Ecological Risk Assessment (1998), to characterize ecological effects associated with a stressor, assessors do the following:
- Describe the effects elicited by the stressor.
Conduct an ecological response analysisIn an ecological risk assessment, this is where the relationship between the stressor and the ecological effects elicited is quantified, and cause--and-effect relationships are evaluated. to evaluate how the magnitude of effects changes with varying stressor levels and the evidence that the stressor causes the effect. The ecological response analysis examines three primary elements:
- Relationships between stressor levels and ecological effects (stressor-response analysis);
- Plausibility that effects may occur or are occurring as a result of exposure to stressors (i.e., establishing cause-and-effect relationships or causality); and
- Linkages between measurable ecological effects and assessment endpoints when the latter cannot be directly measured.
- Prepare a stressor-response profileThe product of characterization of ecological effects in the analysis phase of ecological risk assessment. The stressor-response profile summarizes the data on the effects of a stressor and the relationship of the data to the assessment endpoint. to summarize the data on the effects of a stressor and the relationships of the data to assessment endpointAn explicit expression of the environmental value to be protected, operationally defined as an ecological entity and its attributes.. The stressor-response profile relates the magnitude of an effect to the magnitude, duration, frequency, and timing of exposure.
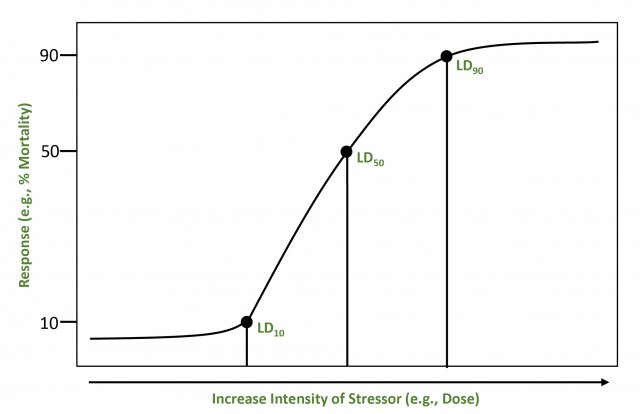
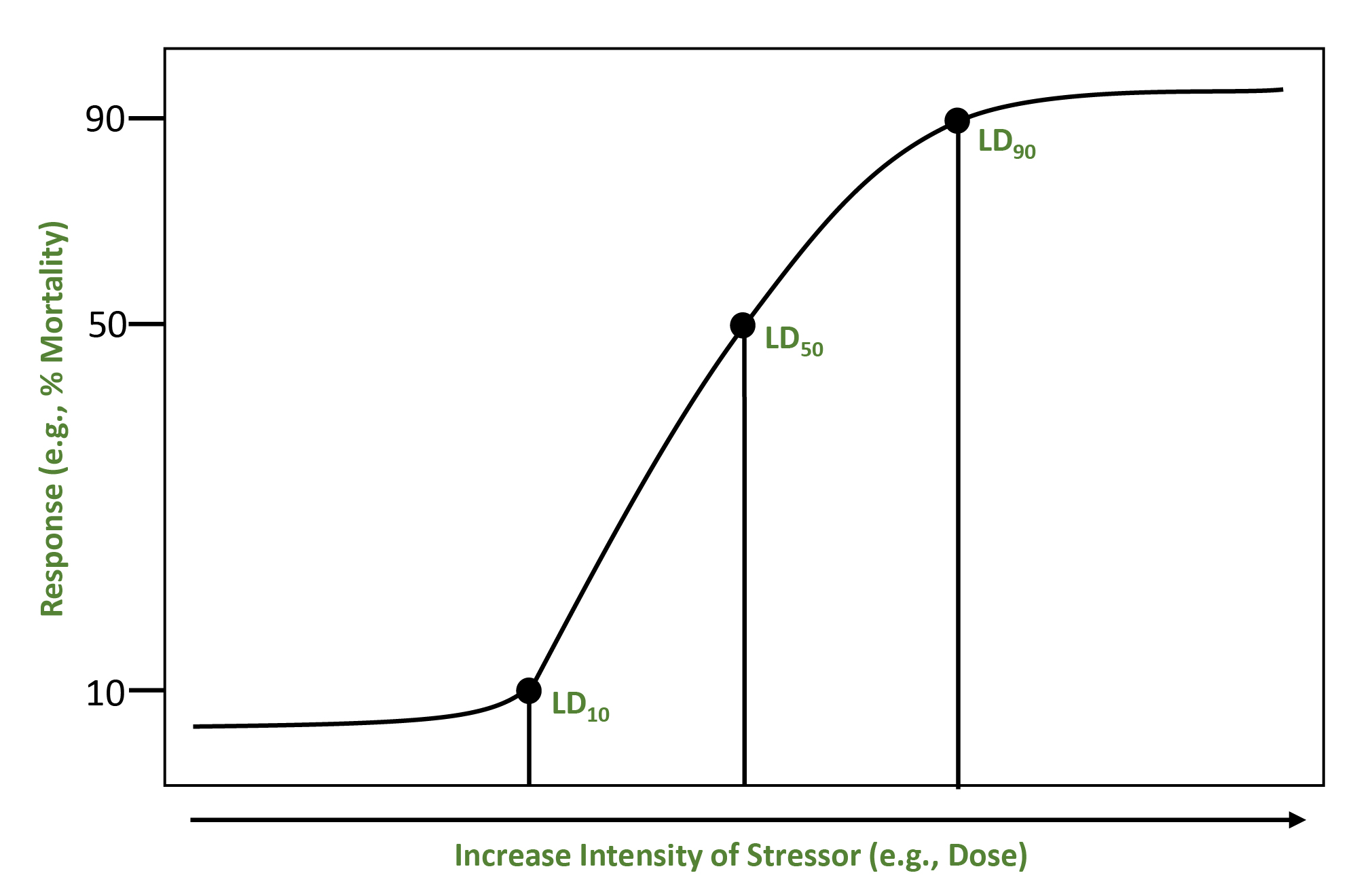
For narrowly defined assessments of a single stressor and effect, the calculated relationship may be expressed as a stressor-response curveA graphic, quantitative representation of the relationship between a stressor and an ecological effect. or summarized as a single reference value (a point on the curve [e.g., LD50]). In many cases, however, more complex interrelationships are present. Effect levels can be expressed in terms of lethality (e.g., LC50 or LD50) or effects other than lethality like growth and reproduction (e.g., EC50 or ED50). In conducting a toxicity test, an assessor might choose to establish no-effect stressor level (e.g., NOAEL) or lowest-effect stressor level (e.g., LOAEL) based on comparisons between experimental treatments and controls.
Below is a simple example of a stressor-response curve that shows a range of responses for increasing stressor intensity. The points represent lethal dose (LD) levels for a given percent of the population. The shape of the stressor-response curve may be needed to determine the presence or absence of thresholdsA concentration above which some effect (or response) will be produced and below which it will not. for significant effects or to evaluate incremental risks (U.S. EPA, 1998). The lower bound of a threshold would be based on consistent conservative assumptions and NOAEL toxicity values. The upper bound would be based on observed impacts or predictions that ecological impacts could occur. This upper bound would be developed using consistent assumptions, site-specific data, LOAEL toxicity values, or an impact evaluation (U.S. EPA, 1997; 1996).
EPA estimates the toxicity or hazard of a stressor by evaluating ecological effects tests that vary from short-term (acute) to long-term (chronic) laboratory studies and might also include field studies. In these tests, animals and plants are exposed to different amounts of a stressor, and their responses to these varying concentrations are measured. The results of these tests may be used to establish a dose-response or cause-and-effect relationship between the amount of stressor to which the organism is exposed and the effects on the organism.
Some of the impacts or ecological effects that are measured in ecotoxicity tests include:
- mortality,
- reduction in growth,
- reproductive impairment,
- changes in numbers of species,
- bioaccumulation of residues in non-target organisms, and
- disruption of community and ecosystem-level functions.
The table below provides examples of toxicity endpoints that might be used in a screening assessment to calculate risk for aquatic and terrestrial receptors.
| Assessment Type | Example Endpoint | Ecological Effects Test Guidelines1 |
|---|---|---|
| Aquatic | ||
| Acute aquatic assessment | Lowest tested EC50 or LC50 for freshwater fish and invertebrates and estuarine/marine fish and invertebrates from acute toxicity tests. | OCSPP 850.1010 Aquatic Invertebrate Acute Toxicity Test, Freshwater Daphnids OCSPP 850.1075 Freshwater and Saltwater Fish Acute Toxicity |
| Chronic aquatic assessment | Lowest NOAEL for freshwater fish and invertebrates and estuarine/marine fish and invertebrates from early life-stage or full life-cycle tests. | OCSPP 850.1300 Daphnid Chronic Toxicity Test OCSPP 850.1400 Fish Early Life Stage Toxicity Test |
| Aquatic vascular plant and algae | Lowest EC50 for vascular and algae. | OCSPP 850.4400 Aquatic Plant Toxicity Test Using Lemna spp. OCSPP 850.4500 Algal Toxicity |
| Terrestrial | ||
| Acute avian assessment | Lowest LD50 (single oral dose) and LC50 (subacute dietary). | OCSPP 850.2100 Avian Acute Oral Toxicity Test OCSPP 850.2200 Avian Dietary Toxicity Test |
| Chronic avian assessment | Lowest NOAEL for 21-week avian reproduction test. | OCSPP 850.2300 Avian Reproduction Test |
| Acute mammalian assessment | Lowest LD50 from single oral dose test. | OCSPP 850.2400 Wild Mammal Toxicity Testing |
| Chronic mammalian assessment | Lowest NOAEL for two-generation reproduction test. | OCSPP 850.2400 Wild Mammal Toxicity Testing |
| Terrestrial non-endangered plant | Lowest EC25 values from both seedling emergence and vegetative vigor for monocots and dicots. | OCSPP 850.4150 Vegetative Vigor |
| Terrestrial endangered plant | Lowest EC5 or NOAEL for both seedling emergence and vegetative vigor for monocots and dicots. | OCSPP 850.4150 Vegetative Vigor |
1Ecological Effects Test Guidelines (Series 850) are available at Series 850 - Ecological Effects Test Guidelines.
Literature reviews, laboratory toxicity tests, and field studies are measure-of-effect tools to help link contaminant concentrations to effects on ecological receptors (see table). These tools provide “dose-response” information: that is, how much toxicant is associated with how much of an adverse effect (U.S. EPA, 1991). Adverse ecological effects are changes that are considered undesirable because they alter valued structural or functional characteristics of ecosystems or their components. An evaluation of adversity may consider the type, intensity, and scale of the effect as well as the potential for recovery (U.S. EPA, 1998).
| Measure of Effect | Considerations |
|---|---|
| Literature reviews | Literature reviews can provide specific dose-response information for a particular receptor. By comparing measured concentrations of contaminants in site media with literature values for adverse effects, investigators can decide whether they need to proceed with site-specific field studies or toxicity tests (U.S. EPA, 1991). |
| Laboratory toxicity tests | Toxicity tests evaluate the effects of stressors on the survival, growth, reproduction, and metabolism of test species. In reviewing test results along with data on stressor levels and biological observations from field studies, ecologists might find evidence that observed or predicted effects are attributable to the presence of the stressor. Toxicity tests could be used to demonstrate spatial extent of contamination and identify areas of high contaminant concentrations (U.S. EPA, 1991; 1994a; 1994b). Because conditions can be controlled in laboratory studies, responses may be less variable and smaller differences easier to detect. However, the controls may limit the range of responses (e.g., animals cannot seek alternative food sources), so they may not reflect responses in the environment. In addition, there are multiple stressors in natural systems and larger-scale processes are difficult to replicate in the laboratory. Frequently, risk assessors extrapolate from laboratory toxicity test data to field effects (U.S. EPA, 1998). |
| Ecological field studies | Ecological field studies (surveys) offer direct or corroborative evidence of a link between a stressor and ecological effects. Evidence could include: reduction in population sizes of species, absence of species normally occurring in the habitat, presence of species associated primarily with stressed habitats, changes in community diversity or trophic structure, and incidence of lesions, tumors, or other pathologies. Ecologists might compare data on observed adverse effects to information obtained from a reference area not affected by the stressor (U.S. EPA, 1991; 1994c). Field studies measure biological changes in uncontrolled situations. Field surveys usually represent exposures and effects (including secondary effects) better than estimates generated from laboratory studies or theoretical models. Field data are more important for assessments of multiple stressors or where site-specific factors significantly influence exposure. They are also often useful for analyses of larger geographic scales and higher levels of biological organization. Risks to organisms in field situations are best estimated from studies at the site of interest. However, such data are not always available. Field surveys are most useful for linking stressors with effects when stressor and effect levels are measured concurrently. The presence of confounding factors can make it difficult to attribute observed effects to specific stressors (U.S. EPA, 1998). |
Risk Characterization: Quantifying Effects in Ecological Risks
The risk characterization quantifies the links between exposure to stressorsAny physical, chemical, or biological entity that can induce an adverse response (synonymous with agent). and effects to ecological receptors and characterizes the types, extent, and severity of those risks. Completing risk characterization allows risk assessors to reach conclusions regarding the occurrence of exposure and the adversity of existing or anticipated effects (U.S. EPA, 1998).
During risk characterization, exposure and stressor-response profilesThe product of characterization of ecological effects in the analysis phase of ecological risk assessment. The stressor-response profile summarizes the data on the effects of a stressor and the relationship of the data to the assessment endpoint. are integrated through the risk estimation process. The final product is a risk description in which the results of the integration are presented, including an interpretation of ecological adversity and descriptions of uncertainty and lines of evidence. The acceptability of adverse effects is determined by risk managers. In characterizing adversity, primary (direct) and secondary (indirect) effects are considered, and sometimes the impact of the secondary effects can outweigh that of the primary effect (U.S. EPA, 1998).
A common approach to quantifying ecological risks to receptors is to compare exposure concentrations of a stressor in an environmental medium by a toxicity reference value (TRV)—a concentration which if exceeded is expected to result in adverse ecological effects. Where exposure-response functions are not available or developed, the quotient method of comparing an estimated exposure concentration to a threshold for response can be used (U.S. EPA, 1997). Typically, the ratio (or quotient) is expressed as an exposure concentration divided by an effects concentration. Quotients are commonly used for chemical stressors for which reference or benchmark toxicity values are widely available (U.S. EPA, 1998).
References
- Hill, AB. (1965). The environment and disease: Association or causation? Proc R Soc Med 58: 295-300.
- U.S. EPA. (1991). ECO update, volume 1, number 2 (8 pp, 202 K, About PDF) [EPA Report]. Office of Solid Waste and Emergency Response.
- U.S. EPA. (1994a). ECO update, volume 2, number 1 (12 pp, 264 K, About PDF) [EPA Report]. Office of Solid Waste and Emergency Response.
- U.S. EPA. (1994b). ECO update, volume 2, number 2 (4 pp, 58 K, About PDF) [EPA Report]. Office of Solid Waste and Emergency Response.
- U.S. EPA. (1994c). ECO update, volume 2, number 3 (14 pp, 152 K, About PDF) [EPA Report]. Office of Solid Waste and Emergency Response.
- U.S. EPA. (1996). ECO update, volume 3, number 2 (12 pp, 192 K, About PDF) [EPA Report]. Office of Solid Waste and Emergency Response.
- U.S. EPA. (1997). Ecological risk assessment guidance for superfund: Process for designing and conducting ecological risk assessments - Interim final [EPA Report]. (EPA/540/R-97/006). Office of Solid Waste and Emergency Response.
- U.S. EPA. (1998). Guidelines for ecological risk assessment [EPA Report]. (EPA/630/R-95/002F). Washington, DC: U.S. Environmental Protection Agency, Risk Assessment Forum.
- U.S. EPA. (2005). Guidance for developing ecological soil screening levels [EPA Report]. (OSWER Directive 9285.7-55). Office of Solid Waste and Emergency Response.
- U.S. EPA. (2011a). Policy assessment for the review of the secondary national ambient air quality standards for oxides of nitrogen and oxides of sulfur (345 pp, 14.2 MB, About PDF) [EPA Report]. (EPA-452/R-11-004a).
- U.S. EPA. (2011b). Review of the national ambient air quality standards for lead: risk and exposure assessment planning document (60 pp, 938 K, About PDF) [EPA Report]. (EPA-452/P-11-003).
- U.S. EPA. (2013). Integrated science assessment for lead: Final report [EPA Report]. (EPA/600/R-10/075F). Washington, DC.
Tools
Resources that provide information related to effects in ecological risk assessments are provided below.