EPA EcoBox Tools by Exposure Pathways - Water and Sediment
Overview

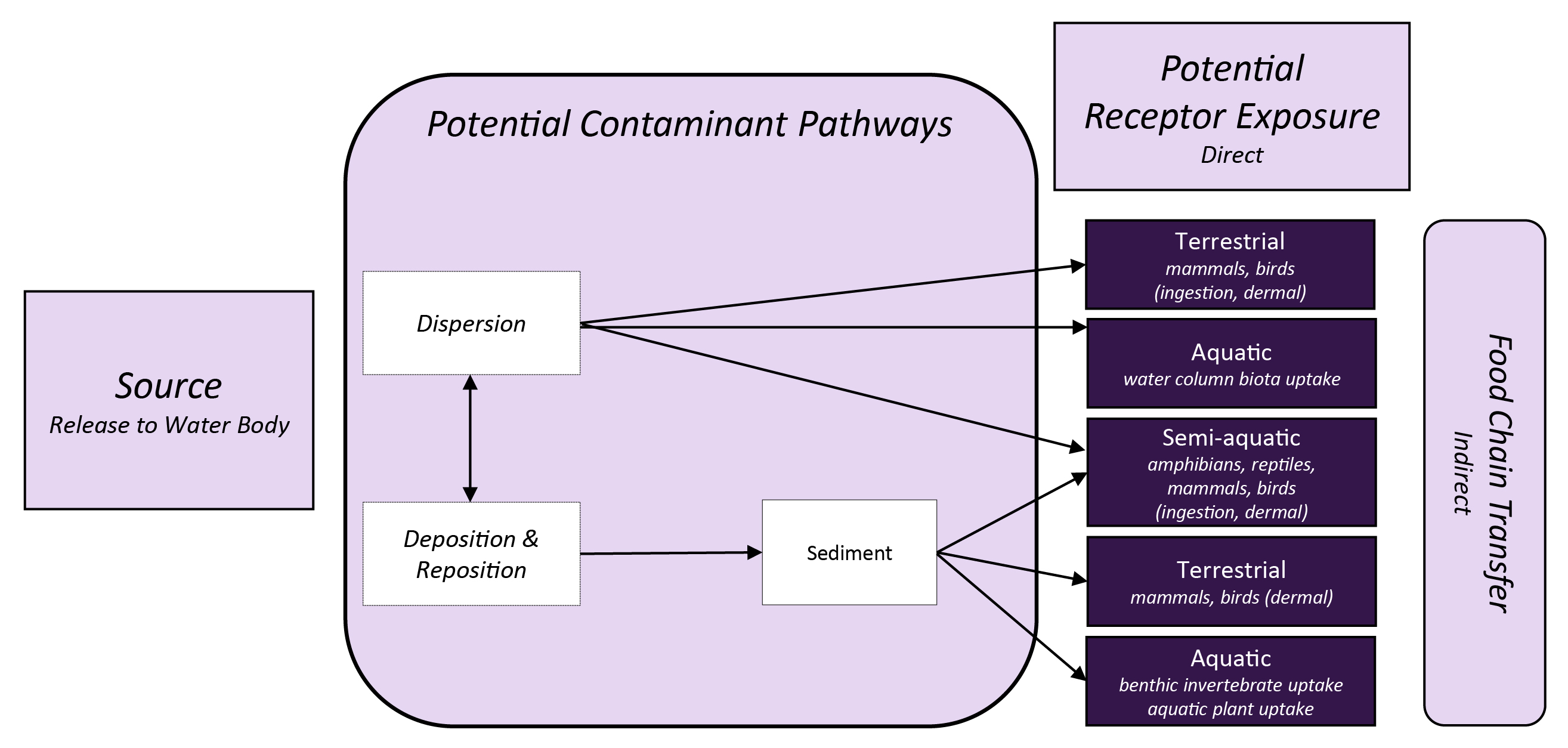
Exposure to contaminants in water and sediment can occur by ingestion (direct or incidental) and dermal contact. Indirect exposure occurs for animals that consume contaminated food and these contaminants can be transferred up the food chain. For example:
- Aquatic animals such as fish are exposed to contaminants in the water column. Exposure could occur via direct uptake from water through gills and accumulation in muscle, fat, and other tissues.
- Fish (particularly bottom dwellers) and shellfish can be exposed to contaminants in sediment.
- Stressors in sediment could be taken up by benthic (i.e., bottom-dwelling) organisms and aquatic plants.
- Semi-aquatic and terrestrial animals might be exposed to contaminants in water bodies while swimming or drinking.
Physicochemical factors can affect the bioavailabilityThe rate and extent to which an agent can be absorbed by an organism and is available for metabolism or interaction with biologically significant receptors. Bioavailability involves both release from a medium (if present) and absorption by an organism. of the contaminant to aquatic biota. These include water solubility and partition coefficients that dictate whether the chemical will be available for uptake from the water column (through consumption or direct transfer from the water) or from aquatic sediments.
The diagram below illustrates relationships between potential exposure pathways and potential ecological receptors after a source releases a stressor to aquatic systems.
Tools
Resources are provided below to assess exposure to ecological receptors that occurs via water or sediment.