Steam Electric Power Generating Effluent Guidelines

The EPA promulgated the Steam Electric Power Generating Effluent Guidelines and Standards (40 CFR Part 423) in 1974, and amended the regulations in 1977, 1978, 1980, 1982, 2015, 2020, and 2024. The regulations cover wastewater discharges from power plants operating as utilities. The Steam Electric regulations are incorporated into NPDES permits.
On this page:
What is Steam Electric Power Generating?
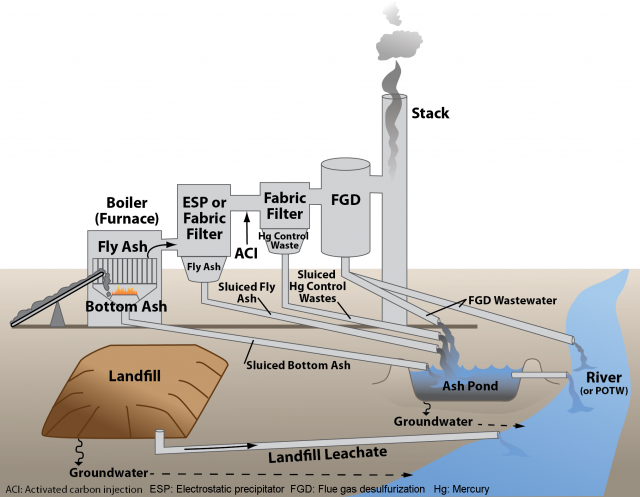
Steam electric plants use nuclear or fossil fuels (such as coal, oil and natural gas) to heat water in boilers, which generates steam. The steam is used to drive turbines connected to electric generators. The plants generate wastewater in the form of chemical pollutants and thermal pollution (heated water) from their water treatment, power cycle, ash handling and air pollution control systems, as well as from coal piles, yard and floor drainage, and other miscellaneous wastes.
- 221112 – Fossil Fuel Electric Power Generation
- 221113 – Nuclear Electric Power Generation
Note: the NAICS group listings are provided as a guide and do not define the coverage of the Steam Electric regulations. For precise definitions of coverage, see the applicability sections in 40 CFR Part 423.
Health and Environmental Impacts of Steam Electric Power Plant Discharges
Steam electric power plants discharge large volumes of wastewater containing pollutants into waters of the United States. The discharges include toxic and bioaccumulative pollutants (selenium, mercury, arsenic, nickel), halogen compounds (bromide, chloride, iodide), nutrients, and total dissolved solids which can cause health and environmental harm through surface water and fish tissue contamination. The pollutants discharged by this industry can cause severe health and environmental problems in the form of cancer and non-cancer risks in humans, lowered IQ among children, and deformities and reproductive harm in fish and wildlife. Many of these pollutants, once in the environment, remain there for years. Due to their close proximity to these discharges and relatively high consumption of fish, some minority and low-income communities have greater exposure to, and are, therefore, at greater risk from, pollutants in steam electric power plant discharges.
There are affordable technologies that are widely available, and already in place at some plants, which reduce or eliminate steam electric power plant discharges. By employing improved technologies to reduce pollutant discharges of wastewater through effluent limitations, potential health benefits come in the form of reduced morbidity and mortality, lower cancer rates, increased IQ among children, and improved water quality. The ecological impacts from reducing power plant discharges include habitat benefits for fresh and saltwater plants, invertebrates, fish, and amphibians, as well as for terrestrial wildlife and birds that prey on aquatic organisms. Overall, implementing wastewater limitations on the steam electric power plants provides benefits to society by enhancing surface water quality and reducing health risks.
Facilities Covered
The Steam Electric Power Generating Effluent Guidelines apply to a major portion of the electric power industry. These are plants primarily engaged in the generation of electricity for distribution and sale which results primarily from a process utilizing fossil-type fuel or nuclear fuel in conjunction with a thermal cycle employing the steam water system as the thermodynamic medium. There are approximately 914 of these facilities located throughout the United States.
Deadline Extensions Rule
The EPA's action extends compliance deadlines for the ELGs that apply to coal-fired power plants.
- Deadlines Extension Rule (December 23, 2025)
2024 Final Rule
The EPA finalized a supplemental rulemaking to strengthen discharge limits for flue gas desulfurization wastewater, bottom ash transport water, combustion residual leachate, and legacy wastewaters.
- 2024 Final Rule (April 24, 2024)
2020 Reconsideration Rule
- 2020 Final Rule (October 13, 2020)
2015 Final Rule
- Final Rule (November 3, 2015)
Background Documents
2009 Detailed Study
Laboratory Analysis of Flue Gas Desulfurization (FGD) Wastewater
Rulemaking History
2024 Amendment
- Final Rule (April 24, 2024)
2020 Amendment
- Final Rule (October 13, 2020)
2015 Amendment
- Final Rule (November 3, 2015)
1982 Amendment
- Documents, including:
- Final Rule (November 19, 1982)
- Development Document
Industry description, wastewater characterization, treatment technologies, regulatory compliance cost estimates, and pollutant loadings for the final rule
- Development Document
- Proposed Rule (October 14, 1980)
- Final Rule (November 19, 1982)
1978 and 1980 Amendments
- Documents, including:
- Final Rule (September 17, 1980)
- Final Rule (September 29, 1978)
1977 Amendment
- Documents, including:
- Final Rule (March 23, 1977)
- Development Document (Pretreatment Supplement)
- Proposed Rule (October 8, 1974)
- Final Rule (March 23, 1977)
1974 Initial Rulemaking
- Documents, including:
- Final Rule (October 8, 1974)
- Development Document
Industry description, wastewater characterization, treatment technologies, regulatory compliance cost estimates, and pollutant loadings for the final rule
- Development Document
- Proposed Rule (March 4, 1974)
- Final Rule (October 8, 1974)
Related Regulations
- Disposal of Coal Combustion Residuals under Resource Recovery and Conservation Act (RCRA)
- Greenhouse Gas Standards and Guidelines for Fossil Fuel-Fired Power Plants under the Clean Air Act (CAA)
- Mercury and Air Toxics Standards under the CAA
Additional Information
For additional information regarding the Steam Electric Power Generating Effluent Guidelines, please contact Richard Benware (benware.richard@epa.gov) or 202-566-1369.