Stormwater Decontamination, Containment, and Diversion Technologies
Contents:
Note the photos included in this table are non-exhaustive of tools available and useful. If you have suggestions for additional items to be included please contact us.
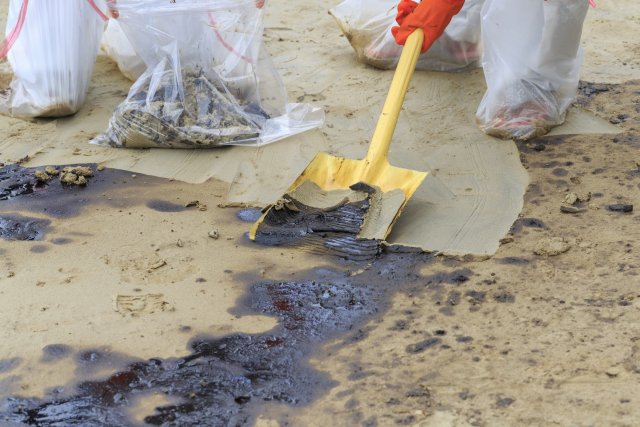

Shovel
A shovel is intended to be used to physically remove the contamination and/or help with installation of containment and diversion equipment. It can also be used as a scrapping device for small areas of concern.
- Cost = $
- Availability = Inventory
- Use = Easy
- Agent = C, B, R
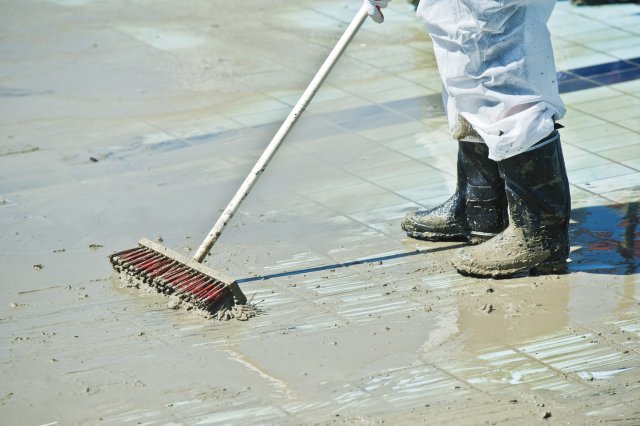

Broom
A broom may be used to aggregate contamination into a centralized location for easier disposal. It can also serve as a method for removing loosely bound contamination and debris prior to application of disinfection.
- Cost = $
- Availability = Inventory
- Use = Easy
- Agent = C,B,R

Squeegee
Squeegees are useful hand tools for removing wet contamination from stormwater impacted infrastructure such as pipes, non-porous channel banks, and roadways.
- Cost = $
- Availability = Inventory
- Use = Easy
- Agent =- C,B,R
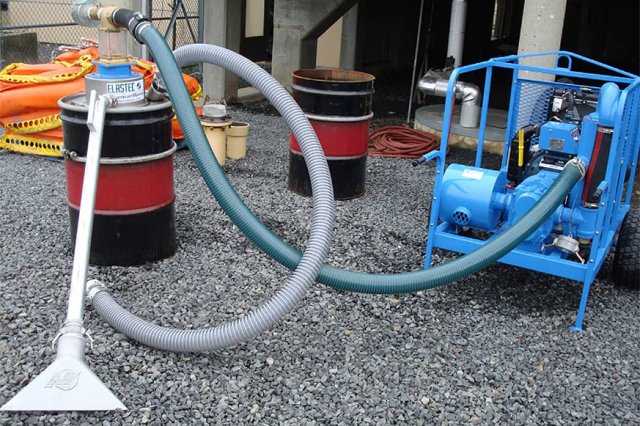

Handheld Suction Devices
Small suction devices such as pool cleaners and portable floating weir skimmers may be used to remove small amounts of contamination from areas such as puddles or from small ponds that a larger vacuum truck cannot get access to. They can collect floating debris and chemicals.
- Cost = $ $
- Availability = Buy/Rent
- Use = Moderate
- Agent = C,B,R
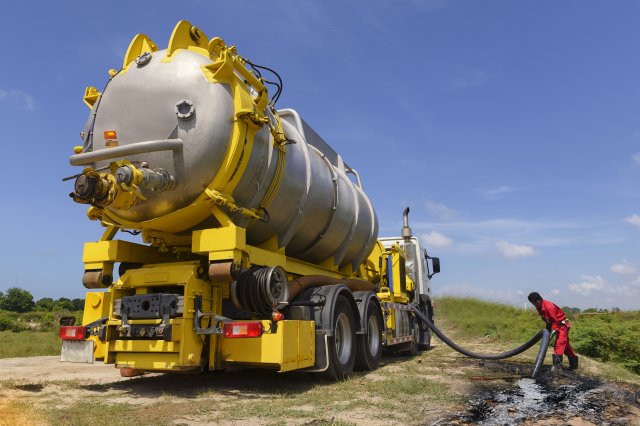

Vacuum Truck
Vacuum trucks are routinely used to fill and empty stormwater storage tanks and collect pressure washing solution when sewer lines are cleaned. They may also be an option for removing large quantities of contaminated water/sludge for transport to a proper disposal facility.
- Cost = $$$$
- Availability = Contractor
- Use = Difficult
- Agent=C,B,R
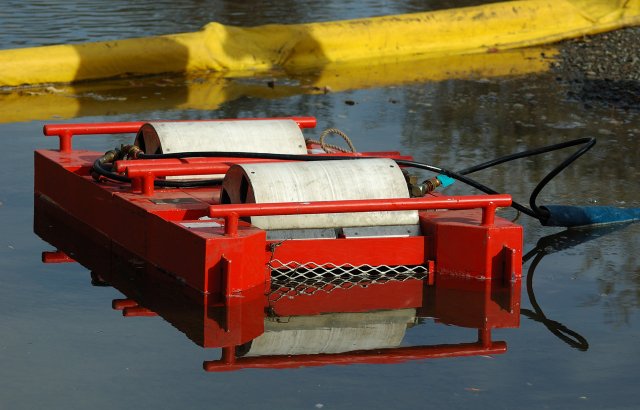

Skimmer
For contaminants that float, a device that sits on the surface of the water such as an oleophilic skimmer which contains sorbant media might be an effective method for removing the contamination. The skimmers must be scraped/squeezed off.
- Cost = $$$
- Availability = Buy/Rent
- Use = Moderate
- Agent=C
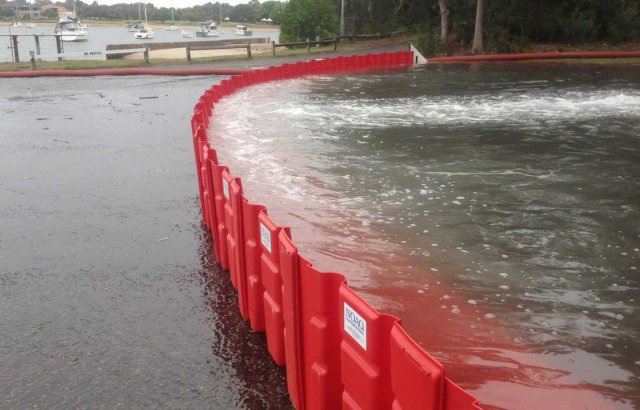

Temporary Walls
Many types of temporary walls are available that are made from a number of different materials including metal and plastic. They may be used for containing flood water or preventing stormwater runoff from entering a waterbody.
- Cost = $ $
- Availability = Buy/Rent
- Use = Easy
- Agent = C,B,R
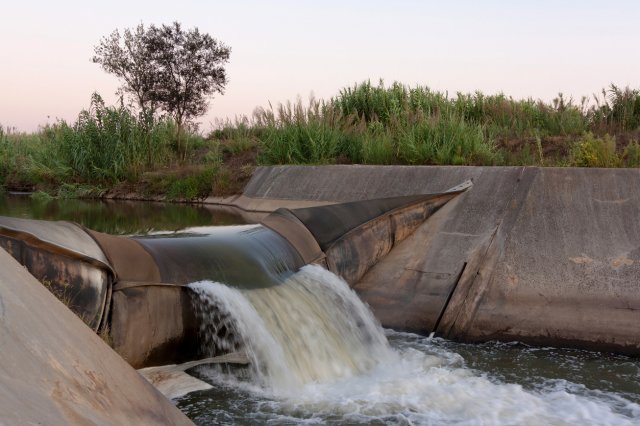

Inflatable Dams
Inflatable dams may be used to slow flow that could scour contamination, provide over-flow or under-flow routes depending on if the contamination sinks or floats, or may be used to block all flow.
- Cost = $ $
- Availability = Inventory
- Use = Moderate
- Agent = C, B, R
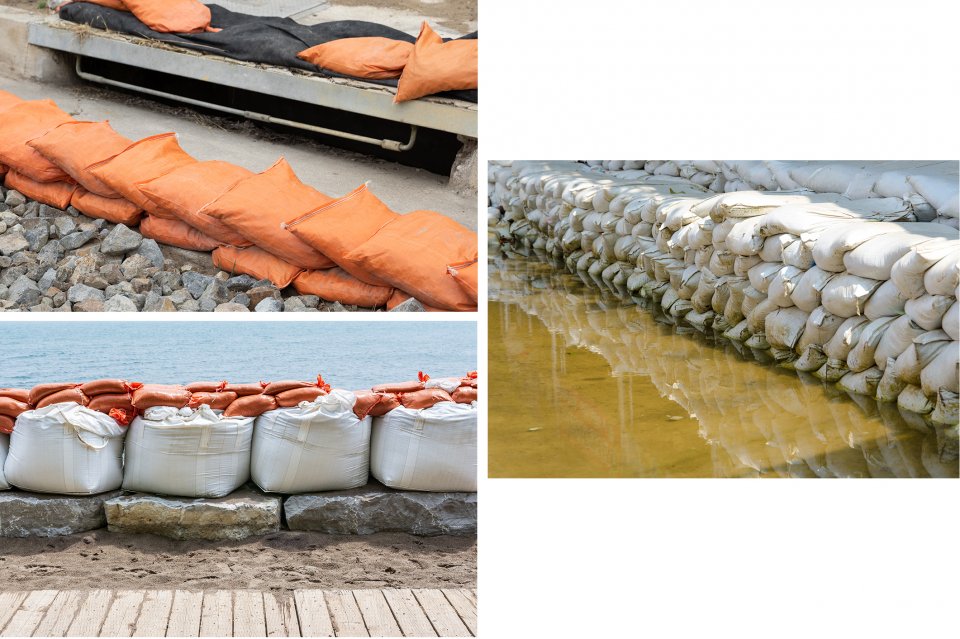

Sand Bags
Sand Bags are a simple technique that may be used to create water barriers. Bag material is typically untreated burlap sacks or polypropylene plastic.
- Cost = $
- Availability = Buy raw materials
- Use = Easy
- Agent = C, B,R
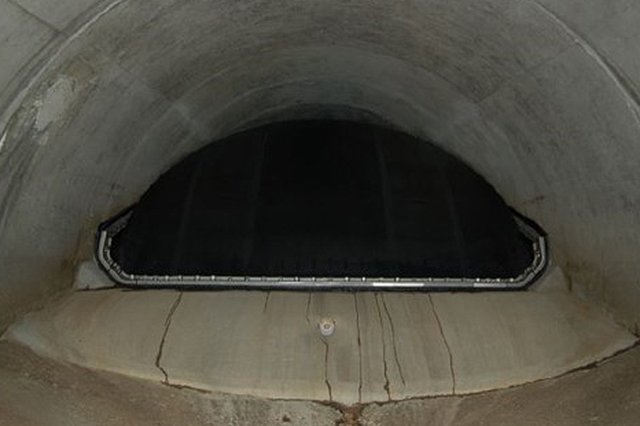

Sewer Plugs
Pipes may be sealed off to prevent the flow of contamination to waterways and/or other portions of the pipe system. Temporary pipe plugs are often inflatable.
- Cost = $ $$
- Availability = Inventory
- Use = Moderate
- Agent = C, B, R
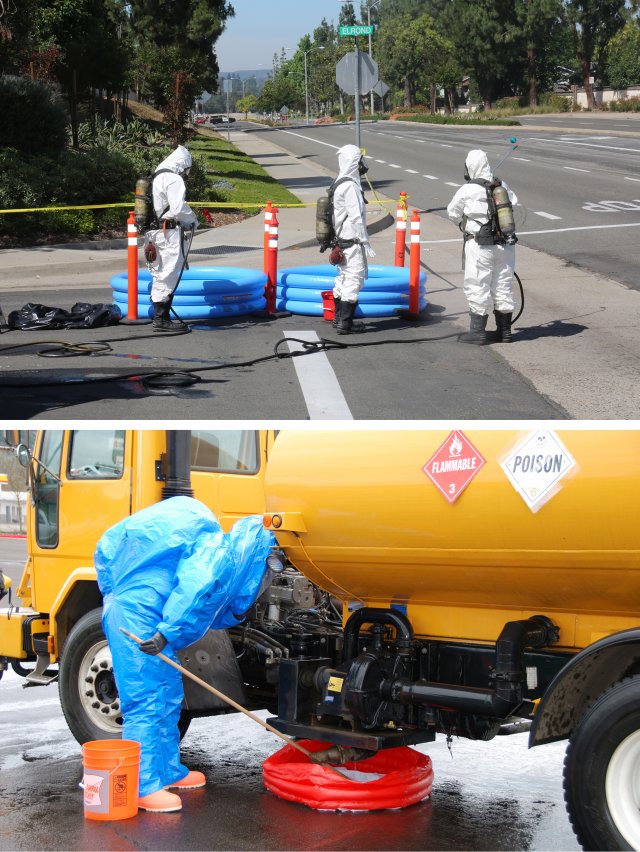

Portable Pools
Pop-up pools may serve as a quick form of containment for small leaks from vehicles or pipes. Larger pools may be placed under cleanup equipment so that it can be decontaminated prior to exiting the contaminated area. Another way that pools may be used is as self-contained cleaning stations for personnel entering and exiting the contaminated area. Larger scale pools are also available to serve as temporary retention basin.
- Cost = $
- Availability = Inventory
- Use = Easy
- Agent = C,B,R
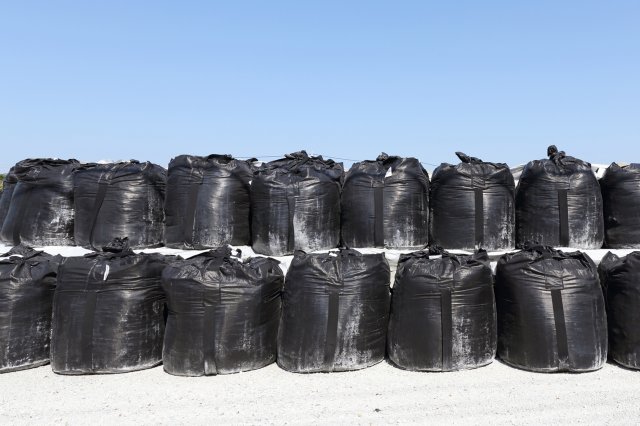

Waste Bags
Decontamination efforts of stormwater impacted infrastructure may generate large volumes of waste. Bags, drums, and totes are often used in interim storage sites. For radiological contamination a layer of uncontaminated soil is often laid on the top to block radiation and waterproof sheets placed to stop rainwater intruding and becoming contaminated. EPA’s Waste Storage and Staging Site Selection Tool may also be useful.
- Cost = $ $$
- Availability = Contractor
- Use = Moderate
- Agent = C, B,R

Liners
Liners help to prevent contaminant migration into the subsurface and spread via groundwater. Liners are particularly useful in areas with high water tables and/or high permeability soils and typically just part of a containment system.
- Cost = $ $$
- Availability = Contractor
- Use = Moderate
- Agent = C, B, R
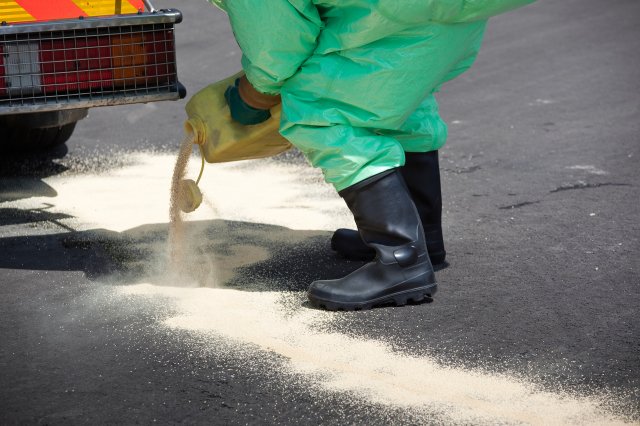

Direct Applied Solid Media
These may be several types of granular or powdered solids that strongly adsorb fluid substances. These can be stockpiled and kept in inventory for emergency use or are widely available at local hardware stores. Common materials used include sand and sawdust. There are a wide variety of adsorbents available with applications to different contaminants.
- Cost = $ $
- Availability = Inventory
- Use = Easy
- Agent = C, R
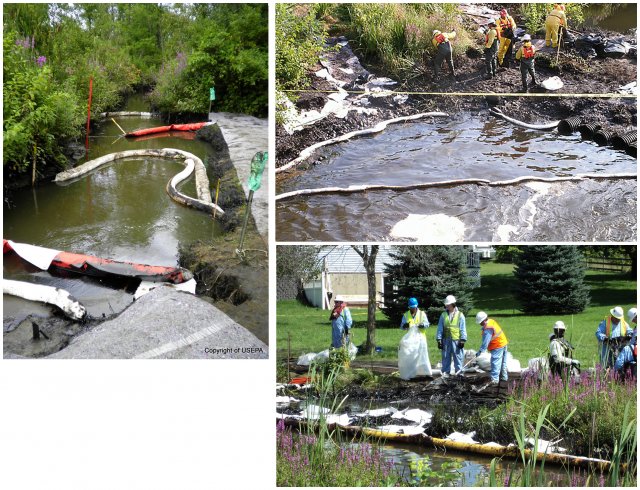
Booms

Mats
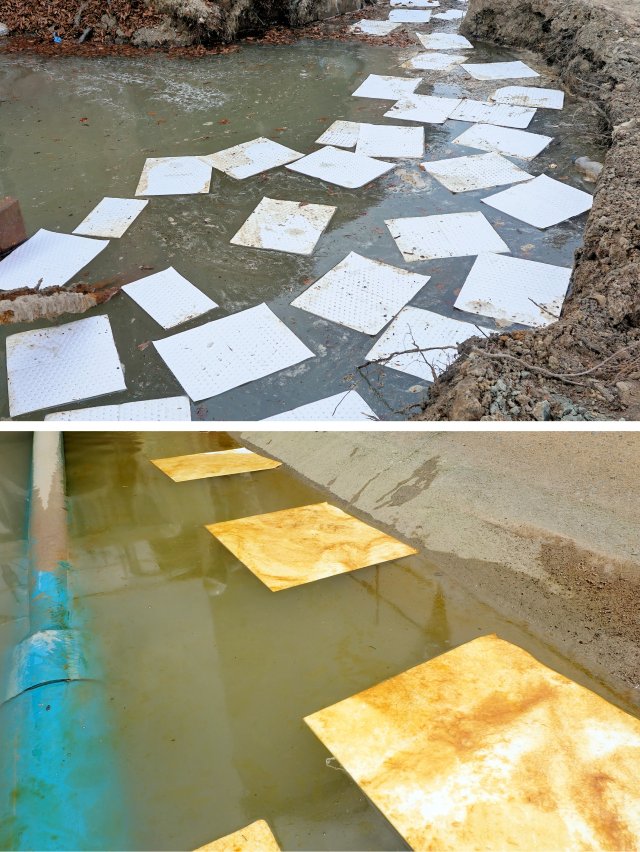

Absorbent Filter Media
Typically absorbs a liquid or fluid, acting much like a sponge focusing on liquid substances rather than particle separation. Absorbent media can be designed for water and petroleum-based liquids or specialized for oil only or hazardous materials. The media can be loose, a boom, mat, pillows or used in combination and easily stockpiled for emergency use. Read more about booms.
- Cost = $ $
- Availability = Inventory
- Use = Easy
- Agent = C, B, R
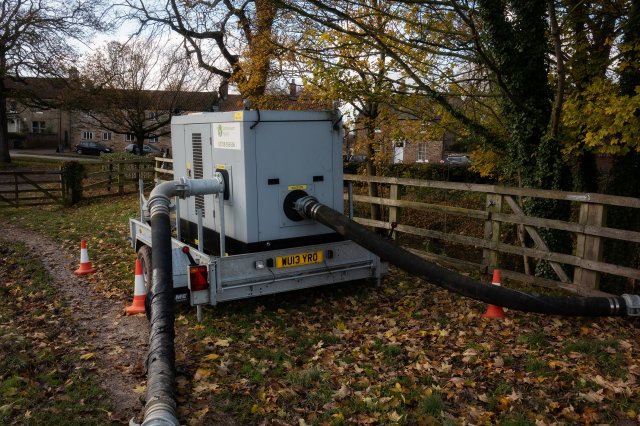

Bypass Pumps
Bypass systems are typically used to re-route or divert uncontaminated fluids away from a spill area or send contaminated fluids to a more controlled area for treatment or hauling away. Larger utilities may have an inventory of various sizes and types of pumps. Small utilities may have to depend on larger systems or pre-arranged agreements with equipment and rental companies to obtain large pumps.
- Cost = $$$$
- Availability = Inventory
- Use = Moderate
- Agent = C, B, R
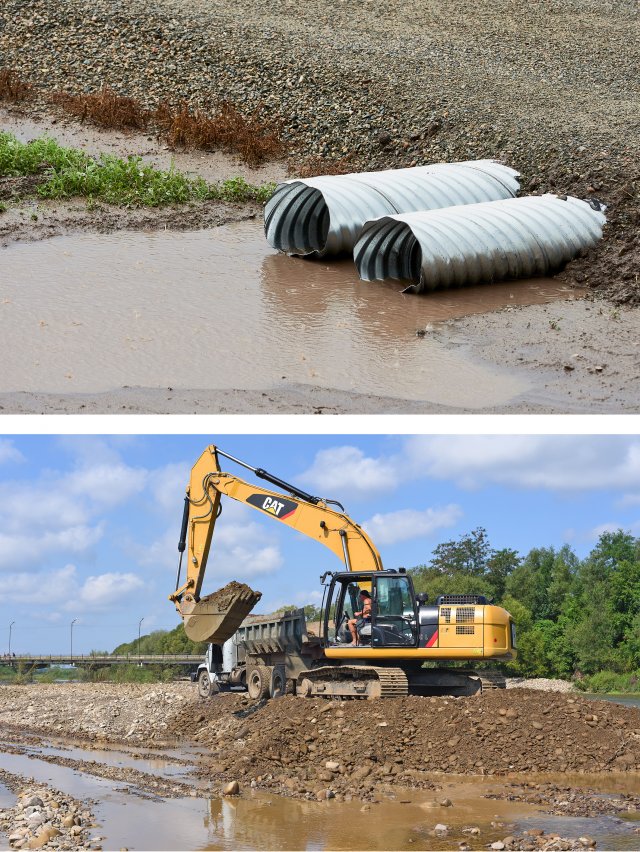

Temporary Culverts & Earth Moving Equipment
Large earth moving equipment utilized for temporary culverts or diversion channels could be owned by larger utilities but as with bypass pumps, contractual arrangements need to be in-place for most utilities.
- Cost = $$$$$
- Availability = Contractor
- Use = Difficult
- Agent = C, B, R
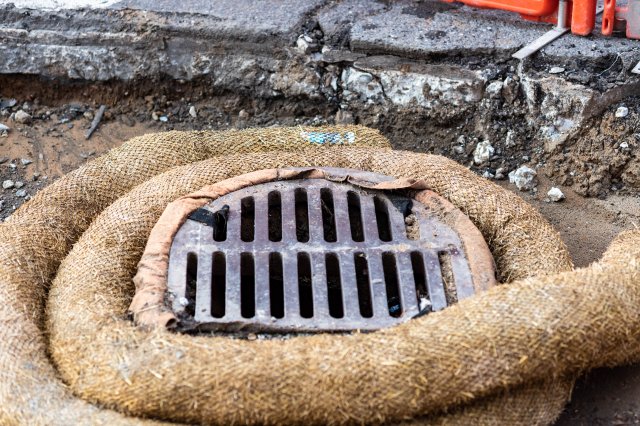

Temporary Berms
Berms and seals are more easily kept in inventory similar to the booms, mats, and media. These, in some instances, can provide some level of water treatment in addition to flow diversion if the berms are constructed of appropriate media.
- Cost = $$
- Availability = Inventory
- Use = Easy
- Agent = C, B, R
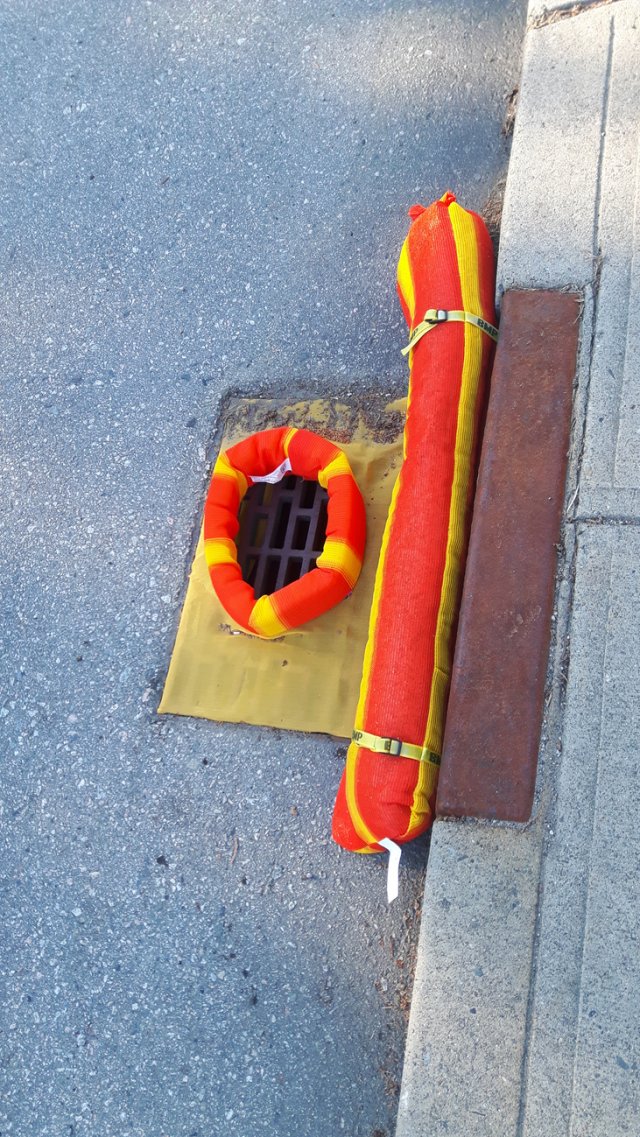

Inlet Seal
Drain seals are typically flexible, non-absorbing material and can effectively prevent gravity flow into drains, manholes, grates, etc. from contaminated water, petroleum, and chemicals for short-term use during an emergency response. Depending on the contamination they may be reusable after cleaning and can be stored in-between uses. Custom sizes and shapes are available and can be stored in custom cases.
- Cost = $$
- Availability = Inventory
- Use = Easy
- Agent = C, B, R
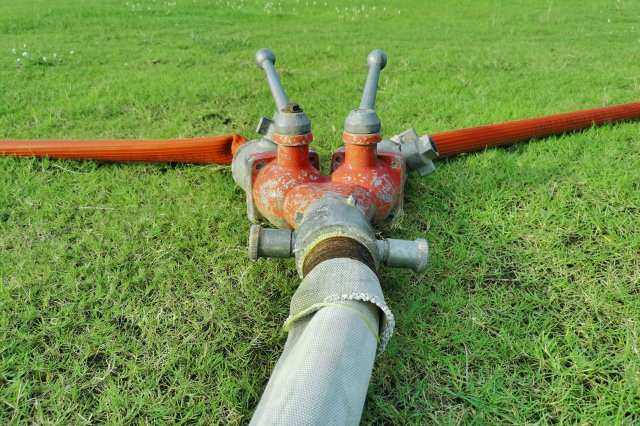

Diverting Valves
Diverting valves can be used as part of a pumping system to convey either non-contaminated water around a contaminated area or contaminated water to multiple other infrastructures (frac tanks, detention basins, etc.) for treatment or to be hauled away. Flow rates can be controlled and used with other valves and pumps.
- Cost = $$$
- Availability = Inventory
- Use = Easy
- Agent = C, B, R
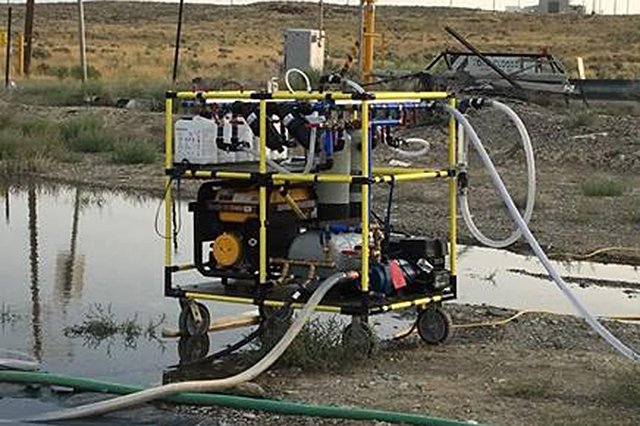

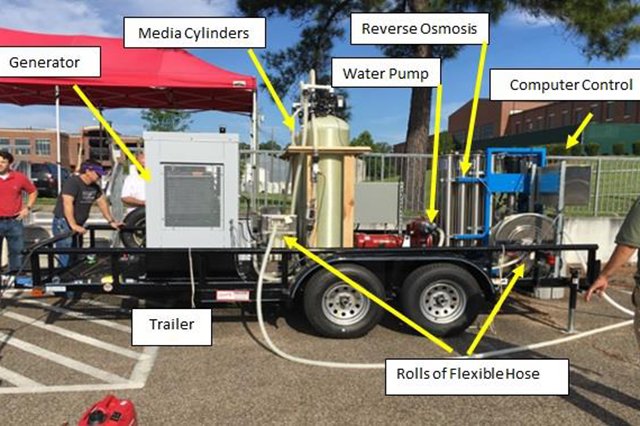
Mobile Treatment Trailers
Mobile water treatment systems can be utilized to improve water quality to be discharged back into the environment or following some level of treatment, shipped for final disposal. Contaminated water can be diverted to temporary holding sites such as frac tanks or detention/retention basins to be held until treated. Commercial vendors offer semi trailer units for rental or purchase that can be customized for treatment objectives. This mobile treatment systems can be relatively costly and difficult to obtain (rent/purchase) in emergency situations. Such items are more likely to be available as part of a Water and Wastewater Agency Response Network (WARN) or available from large Federal emergency operations agencies. Smaller, easier to operate, and more economical mobile systems are now entering the commercial market that could be shared and stored prior to an emergency. Read more about EPA’s mobile emergency water treatment system research.
- Cost = $$$$$
- Availability = Rent
- Use = Moderate-Difficult
- Agent = C, B, R

Catch Basin Inserts
Fixed catch basin inserts can require much lead time if not already installed as water quality and flow control mechanisms as part of routine regulatory compliance. Pre-deployed catch basin retrofits are infrastructure assets that could be modified in an emergency to remove a different type of contaminant, or totally sealed to contain or divert contaminated water.
- Cost = $$$
- Availability = Pre-Install
- Use = Moderate
- Agent = C, B, R

Detention Basin Retrofits
Fixed detention basin retrofits, similar to catch basin inserts would need to be strategically installed prior to an emergency. These fixed installations can provide passive flow modification and targeted contaminant reduction via filtration media built into the devices. These assets may improve stream habitat on a regular basis while being available for emergency response. The devices can be modified to temporarily completely block flow exiting the detention basin to hold extremely contaminated water for treatment or disposal. Read more about EPA’s detention basin retrofit research for wide-area contamination incidents.
- Cost = $$$$
- Availability = Pre-Install
- Use = Moderate
- Agent = C, B, R
If you would like to contribute a photo of a portable chlorinator system that is copyright free please contact us.
Portable Chlorinator Systems
Biological contaminated stormwater may be disinfected with chlorine. Trailer or pickup truck mounted systems are available from commercial vendors that are routinely used for flood water treatment and emergency drinking water disinfection.
- Cost = $$$$
- Availability = Rent
- Use = Moderate
- Agent = B
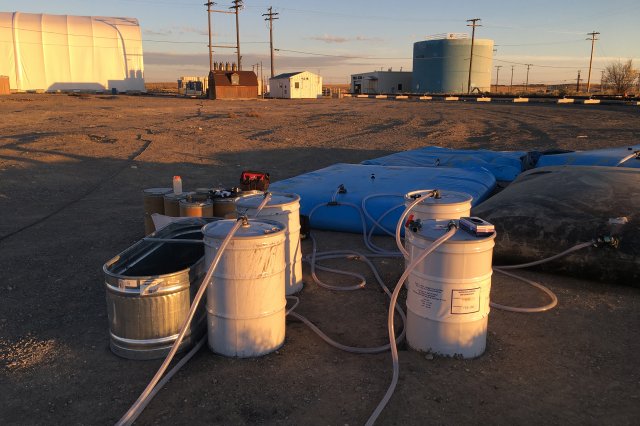

Drum Systems
Multiple vendors sell carbon filtration drum systems that are easily deployable for onsite treatment. Read more about EPA’s research on the treatment of perfluorinated alkyl substances in wash water using granular activated carbon and mixed-media using a drum based system.
- Cost = $$$$
- Availability = Inventory
- Use = Moderate
- Agent = C, B, R
