Energy Production at Superfund Sites
Superfund sites can be well suited for energy production. Sites in urban and rural areas near utilities and transportation networks help keep development costs low and can help communities create jobs and diversify local economies. They are also important to America’s energy security and environmental sustainability. EPA’s Superfund Redevelopment Program supports parties as they work to reuse contaminated lands for a wide range of purposes, including many types of energy production and storage.
On this page:
- Current Status of Alternative Energy Projects at Superfund Sites
- Superfund Site Examples and Case Studies
- Tools and Resources for Energy Reuse
Current Status of Alternative Energy Projects at Superfund Sites
As of 2024, 161 alternative energy installations at 110 Superfund sites have an installed capacity of 1,988 megawatts, enough to power more than 282,232 homes for a year.
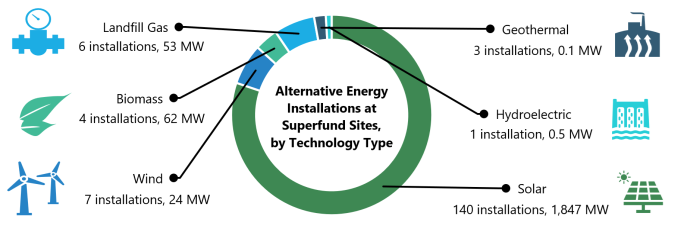

Each year, EPA’s Superfund Redevelopment Program releases a report highlighting alternative energy projects at Superfund sites. The report presents the installed capacity and estimated annual output of the on-site installations.
Superfund Site Examples and Case Studies
Site Spotlight: Gallup's Quarry – Plainfield, Connecticut (EPA Region 1)

The 37.5-megawatt biomass cogeneration plant at the Gallup’s Quarry Superfund site in Plainfield, Connecticut, uses waste wood to generate enough electricity to power the equivalent of about 40,000 homes in Plainfield. The facility provides a market for waste biomass materials that would otherwise be taken to a landfill or left to decay.
Superfund Site Energy Production Reuse Successes:
- Central Landfill – Johnston, Rhode Island (EPA Region 1)
- Picillo Farm – Coventry, Rhode Island (EPA Region 1)
- Sullivan's Ledge – New Bedford, Massachusetts (EPA Region 1)
- Brick Township Landfill – Brick Township, New Jersey (EPA Region 2)
- York County Solid Waste and Refuse Authority Landfill – Stewartstown, Pennsylvania (EPA Region 3)
- Atlantic Phosphates Works – Charleston, SC (EPA Region 4)
- Continental Steel Corp. – Kokomo, Indiana (EPA Region 5)
- Koch Refining Co./N-Ren Corp. – Rosemount, MN (EPA Region 5)
- Southside Sanitary Landfill – Indianapolis, Indiana (EPA Region 5)
- Chevron Questa Mine – Questa, New Mexico (EPA Region 6)
- Tex-Tin Corp. – Texas City, TX (EPA Region 6)
- Oronogo-Duenweg Mining Belt – Joplin, Missouri (EPA Region 7)
- Lowry Landfill – Aurora, Colorado (EPA Region 8)
- Aerojet General Corp – Rancho Cordova, California (EPA Region 9)
- United Chrome Products, Inc. – Corvallis, OR (EPA Region 10)
Energy Production Case Studies
Find in-depth case studies and fact sheets highlighting Superfund sites in energy reuse. In-depth case studies take a start-to-finish look at how sites were returned to use, including a detailed discussion of challenges, strategies for overcoming barriers, key stakeholders, partnerships critical for moving projects forward, and resources secured to turn reuse visions into reality.
| Site Name | State | Region | Type of Report | Year | Reuse Keywords |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aerojet General Corp. | CA | 9 | In-Depth Case Study (pdf) (3.54 MB) | 2010 | industrial; energy; solar; groundwater |
| Aerojet General Corp. | CA | 9 | Site Redevelopment Profile (pdf) (4.28 MB) | 2018 | industrial; energy; solar; commercial; agricultural; ecological; groundwater |
| American Cyanamid Co | NJ | 2 | Beneficial Effects Economic Case Study (pdf) (3.2 MB) | 2018 | recreational; commercial; public service; energy; solar; ecological |
| Barceloneta Landfill | PR | 2 | Video | 2024 | solar; landfill; energy |
| Boise Cascade/Onan Corp./Medtronics, Inc. | MN | 5 | Beneficial Effects Economic Case Study (pdf) (1.52 MB) | 2017 | ecological; commercial; industrial; wood-treating; vapor intrusion; energy; solar |
| Brick Township Landfill | NJ | 2 | In-Depth Case Study (pdf) (6.03 MB) | 2015 | solar; landfill; energy; capped |
| Brunswick Naval Air Station | ME | 1 | Beneficial Effects Economic Case Study (pdf) (3.71 MB) | 2019 | recreational; ecological; commercial; industrial; public service; residential; military; energy; solar; biomass |
| Carson River Mercury Site | NV | 9 | Site Redevelopment Profile (pdf) (1.88 MB) | 2023 | commercial; residential; agricultural; recreational; ecological; solar; mine; mining; energy; capped |
| Charles George Reclamation Trust Landfill | MA | 1 | Site Redevelopment Profile (pdf) (442 KB) | 2017 | solar; landfill; energy |
| Chevron Questa Mine | NM | 6 | In-Depth Case Study (pdf) (6.74 MB) | 2013 | solar; mine; mining; energy |
| Ciba-Geigy Corp. | NJ | 2 | Site Redevelopment Profile (pdf) (2.67 MB) | 2022 | ecological; energy; solar; groundwater |
| Continental Steel Corp. | IN | 5 | In-Depth Case Study (pdf) (4.23 MB) | 2018 | recreational; ecological; public service; energy; solar; wind |
| Continental Steel Corp. | IN | 5 | Site Redevelopment Profile (pdf) (1.15 MB) | 2018 | recreational; energy; solar |
| Continental Steel Corp. | IN | 5 | Video | 2018 | solar; recreational; energy |
| Davisville Naval Construction Battalion Center | RI | 1 | Beneficial Effects Economic Case Study (pdf) (4.37 MB) | 2018 | recreational; ecological; commercial; industrial; public service; military; energy; solar; landfill; wetlands |
| E.I. du Pont de Nemours & Co., Inc. (Newport Pigment Plant Landfill) | DE | 3 | Beneficial Effects Economic Case Study (pdf) (708 KB) | 2014 | recreational; ecological; industrial; energy; solar; landfill |
| Ecosystem Services at Superfund Sites | Multiple | Multiple | Beneficial Effects Economic Case Study (pdf) (30.9 MB) | 2023 | recreational; ecological; agricultural; commercial; military; solar; wind; biomass; geothermal; landfill gas; landfill; mine; mining; energy; capped; tribal |
| Elizabeth Mine | VT | 1 | Site Redevelopment Profile (pdf) (329 KB) | 2019 | ecological; public service; energy; solar; mine; mining; wetlands |
| Fibers Public Supply Wells | PR | 2 | Site Redevelopment Profile (pdf) (2.2 MB) | 2024 | solar; energy; groundwater; industrial; public service |
| Former Nansemond Ordnance Depot | VA | 3 | Beneficial Effects Economic Case Study (pdf) (13.6 MB) | 2023 | commercial; industrial; residential; public service; military; ecological; solar; energy |
| Fort Detrick Area B Ground Water | MD | 3 | Site Redevelopment Profile (pdf) (534 KB) | 2017 | agricultural; public service; energy; solar; landfill; military |
| GE - Housatonic River | MA | 1 | Site Redevelopment Profile (pdf) (1.49 MB) | 2022 | recreational; ecological; commercial; industrial; public service; residential; energy; solar |
| Global Sanitary Landfill | NJ | 2 | Video | 2024 | solar; landfill; energy |
| H.O.D. Landfill | IL | 5 | In-Depth Case Study (pdf) (1.23 MB) | 2014 | recreational; public service; ecological; energy; landfill gas; landfill; wetlands |
| Iron Horse Park | MA | 1 | Beneficial Effects Economic Case Study (pdf) (1.99 MB) | 2017 | ecological; industrial; energy; solar; landfill; wetlands |
| Iron Horse Park | MA | 1 | Site Redevelopment Profile (pdf) (1.86 MB) | 2019 | ecological; industrial; energy; solar; landfill; wetlands |
| Juncos Landfill | PR | 2 | Video | 2024 | solar; landfill; energy |
| Landfill & Development Co. | NJ | 2 | Site Redevelopment Profile (pdf) (383 KB) | 2019 | solar; landfill; ecological; recreational; energy; capped |
| Lexington County Landfill Area | SC | 4 | Video | 2015 | landfill; recreational; public service; landfill gas; groundwater; capped; energy |
| Loring Air Force Base | ME | 1 | Beneficial Effects Economic Case Study (pdf) (5.71 MB) | 2018 | recreational; ecological; commercial; industrial; public service; residential; federal; military; energy; solar |
| Martin-Marietta, Sodyeco, Inc. | NC | 4 | In-Depth Case Study (pdf) (5.66 MB) | 2015 | recreational; ecological; industrial; commercial; agricultural; biomass; energy |
| Martin-Marietta, Sodyeco, Inc. | NC | 4 | Beneficial Effects Economic Case Study (pdf) (1.5 MB) | 2018 | recreational; ecological; industrial; commercial; agricultural; energy; biomass |
| Martin-Marietta, Sodyeco, Inc. | NC | 4 | Site Redevelopment Profile (pdf) (1.5 MB) | 2019 | recreational; ecological; industrial; commercial; agricultural; energy; biomass |
| Maunabo Area Ground Water Contamination | PR | 2 | Video | 2024 | solar; landfill; energy |
| Chevron Questa Mine | NM | 6 | Site Redevelopment Profile (pdf) (135 KB) | 2011 | solar; mine; mining; energy |
| Mosley Road Sanitary Landfill | OK | 6 | Site Redevelopment Profile (pdf) (1.07 MB) | 2018 | landfill gas; landfill; energy |
| North Carolina State University (Lot 86, Farm Unit #1) | NC | 4 | Site Redevelopment Profile (pdf) (1.61 MB) | 2017 | solar; energy |
| North Sanitary Landfill | OH | 5 | Video | 2024 | solar; landfill; energy |
| North Sanitary Landfill | OH | 5 | Video | 2024 | solar; landfill; energy |
| North Sanitary Landfill | OH | 5 | Video | 2024 | solar; landfill; energy |
| Northside Landfill | WA | 10 | Site Redevelopment Profile (pdf) (894 KB) | 2022 | commercial; public service; landfill; solar; energy |
| Northwest Pipe & Casing/Hall Process Company | OR | 10 | Beneficial Effects Economic Case Study (pdf) (1.12 MB) | 2015 | industrial; commercial; public service; energy; solar; wetlands |
| Nyanza Chemical Waste Dump | MA | 1 | Site Redevelopment Profile (pdf) (1.04 MB) | 2022 | ecological; commercial; industrial; energy; solar; landfill; vapor intrusion; groundwater; wetlands |
| Operating Industries, Inc., Landfill | CA | 9 | Site Redevelopment Profile (pdf) (612 KB) | 2022 | commercial; landfill; landfill gas; solar; energy |
| Operating Industries, Inc., Landfill | CA | 9 | Beneficial Effects Economic Case Study (pdf) (1.93 MB) | 2020 | commercial; landfill; landfill gas; solar; energy |
| Operating Industries, Inc., Landfill | CA | 9 | StoryMap (pdf) (NA) | 2019 | landfill; commercial; landfill gas; energy |
| Oronogo-Duenweg Mining Belt | MO | 7 | Site Redevelopment Profile (pdf) (362 KB) | 2023 | residential; recreational; agricultural; commercial; industrial; public service; mine; mining; solar; energy; capped |
| Pantex Plant (USDOE) | TX | 6 | Site Redevelopment Profile (pdf) (1.07 MB) | 2016 | wind; federal; groundwater; energy |
| Parsons Paper Mill | MA | 1 | Site Redevelopment Profile (pdf) (604 KB) | 2022 | industrial; solar; energy |
| Peterson/Puritan, Inc. | RI | 1 | Beneficial Effects Economic Case Study (pdf) (2.21 MB) | 2014 | recreational; commercial; industrial; public service; residential; ecological; federal; energy; solar; landfill |
| Reilly Tar & Chemical Corp. (Indianapolis Plant) | IN | 5 | In-Depth Case Study (pdf) (5.88 MB) | 2014 | solar; wood-treating; landfill; capped; energy |
| Reilly Tar & Chemical Corp. (Indianapolis Plant) | IN | 5 | Beneficial Effects Economic Case Study (pdf) (4.52 MB) | 2023 | residential; industrial; commercial; energy; solar; landfill; capped |
| Re-Solve, Inc. | MA | 1 | Site Redevelopment Profile (pdf) (491 KB) | 2019 | ecological; energy; solar; groundwater; wetlands |
| Rose Hill Regional Landfill | RI | 1 | Site Redevelopment Profile (pdf) (517 KB) | 2019 | public service; energy; solar; landfill; capped |
| Solvents Recovery Service of New England | CT | 1 | Site Redevelopment Profile (pdf) (740 KB) | 2017 | recreational; energy; solar; groundwater; capped |
| Southside Sanitary Landfill | IN | 5 | Site Redevelopment Profile (pdf) (3.99 MB) | 2019 | recreational; industrial; public service; energy; landfill gas; landfill |
| Southside Sanitary Landfill | IN | 5 | Beneficial Effects Economic Case Study (pdf) (394 KB) | 2011 | recreational; industrial; public service; energy; landfill gas; landfill |
| Strother Field Industrial Park | KS | 7 | Beneficial Effects Economic Case Study (pdf) (1.42 MB) | 2015 | commercial; industrial; public service; solar; landfill; energy; capped |
| Sullivan's Ledge | MA | 1 | In-Depth Case Study (pdf) (3.46 MB) | 2015 | solar; landfill; landfill gas; wind; wetlands; capped; energy |
| Sutton Brook Disposal Area | MA | 1 | Site Redevelopment Profile (pdf) (1.28 MB) | 2022 | ecological; energy; solar; landfill; capped; wetlands |
| Tar Creek (Ottawa County) | OK | 6 | Site Redevelopment Profile (pdf) (819 KB) | 2020 | residential; commercial; public service; agricultural; ecological; mine; mining; solar; recreational; energy; wetlands; tribal |
| Tar Creek (Ottawa County) | OK | 6 | Video | 2024 | tribal; energy; solar |
| Tar Creek (Ottawa County) | OK | 6 | Video | 2024 | tribal; energy; solar |
| Tucson International Airport Area | AZ | 9 | Beneficial Effects Economic Case Study (pdf) (1.63 MB) | 2016 | industrial; commercial; federal; military; public service; energy; solar; groundwater; landfill |
| Vega Baja Solid Waste Disposal | PR | 2 | Video | 2024 | energy; solar; landfill |
| Ventron/Velsicol | NJ | 2 | Beneficial Effects Economic Case Study (pdf) (3.28 MB) | 2021 | recreational; ecological; commercial; industrial; energy; solar; vapor intrusion; capped |
| W.R. Grace & Co., Inc. (Acton Plant) | MA | 1 | Site Redevelopment Profile (pdf) (1.14 MB) | 2017 | energy; solar; ecological; landfill; capped; wetlands |
| Welsbach & General Gas Mantle (Camden Radiation) | NJ | 2 | Site Redevelopment Profile (pdf) (947 KB) | 2020 | recreational; commercial; industrial; public service; energy; solar |
| Welsbach & General Gas Mantle (Camden Radiation) | NJ | 2 | Beneficial Effects Economic Case Study (pdf) (4.34 MB) | 2020 | recreational; commercial; industrial; public service; energy; solar |
| West Kingston Town Dump/URI Disposal Area | RI | 1 | Site Redevelopment Profile (pdf) (924 KB) | 2019 | recreational; energy; solar; landfill; capped |
| York County Solid Waste and Refuse Authority Landfill | PA | 3 | Site Redevelopment Profile (pdf) (297 KB) | 2019 | recreational; ecological; energy; solar; landfill; public service; capped |
Tools and Resources for Energy Reuse
Superfund Redevelopment Program Tools and Resources

Reuse Opportunities at Capped Superfund Sites (pdf) (5.3 MB)
This report discusses leading examples of capped-area reuses, including energy uses, across the country, highlighting recent trends, key factors and other considerations that make these uses possible.
Renewable and Alternative Energy at Superfund Sites: Harnessing New Sources of Power (pdf) (5 MB)
This report provides technical information and case studies illustrating opportunities for renewable and alternative energy projects at Superfund sites.
Technical Assistance and Reuse Planning Support
EPA’s Superfund Redevelopment Program provides reuse planning and technical assistance to communities, stakeholders and EPA’s Regions to support the productive reuse and redevelopment of Superfund sites. These Regional Support Projects aim to facilitate redevelopment, remove barriers to productive reuse, and make sure that future uses at Superfund sites are well aligned with cleanups and long-term remedies. These projects can focus on specific areas at a Superfund site or include a much larger neighborhood or surrounding area.
Technical assistance and reuse planning support includes a variety of activities. They can be structured as stand-alone, just-in-time services or as part of a longer-term redevelopment support process. EPA’s Superfund Redevelopment Program tailors technical assistance and reuse planning activities to address each site and the needs of EPA site teams, stakeholders and communities.
Examples of Superfund Redevelopment Support
The Superfund Redevelopment Program supports feasibility studies and assessments to determine the potential for energy reuse.
- Preliminary Assessment of Renewable Energy Opportunities – Naval Weapons Industrial Reserve Plant (pdf) (10.1 MB)
- Preliminary Assessment of Renewable Energy Opportunities Somersworth Landfill, Somersworth, New Hampshire (pdf) (1.3 MB)
- Renewable Energy Assessment Prairie View Landfill – Will County, Illinois (pdf) (10.5 MB)
- Renewable Energy Reuse Assessments for Sites in EPA Region 5 (pdf) (6.6 MB)
- Report on Evaluating Renewable Energy Opportunities: The Apache Powder Superfund Site, Benson, Arizona (pdf) (9.2 MB)
- Solar Incentives for Superfund Sites in Puerto Rico (pdf) (922 KB)
EPA’s Re-Powering America’s Land Initiative
EPA’s RE-Powering America’s Land Initiative encourages renewable energy development on current and formerly contaminated lands, landfills and mine sites when such development is aligned with the community’s vision for the site. The Initiative identifies the renewable energy potential of these sites and provides other useful resources for communities, developers, industry, state and local governments or anyone interested in reusing these sites for renewable energy development.
Potentially contaminated land includes sites where contamination is suspected but has not been confirmed and sites where contamination has been identified. Targeted sites include brownfields, Superfund sites, sites subject to corrective action under the Resource Conservation and Recovery Act, mining sites and landfills.
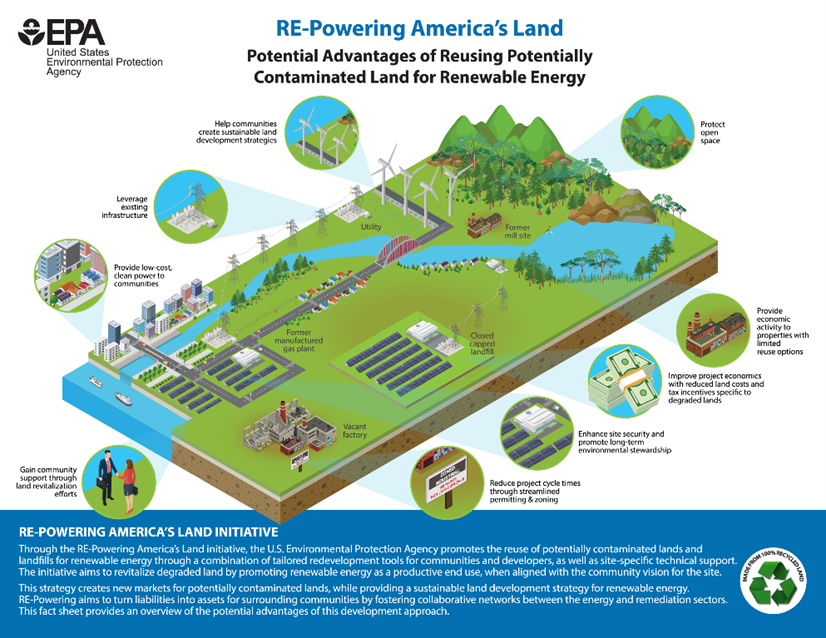
These stories highlight energy installations at current and formerly contaminated lands, landfills and mine sites.
The Matrix tracks completed projects where energy systems are in place at contaminated lands, landfills and mine sites.
EPA maintains a list of economic and environmental benefits reported by communities and developers associated with energy projects on contaminated lands.
Other Tools and Resources
Abandoned Mine Lands: Revitalization and Reuse
This EPA team provides communities with technical support and resources to explore innovative reuse opportunities at former mine sites.
The Brownfields and Land Revitalization Programs
EPA’s Brownfields Program provides grants and technical assistance to communities, states, Tribes and others to assess, safely clean up and reuse contaminated properties. To learn about EPA’s broader efforts to support the return of once-contaminated properties to productive use, check out the agency’s Land Revitalization Program.
These EPA programs provide information and technical assistance for clean energy technologies, energy efficiency, green power resources, and Tribal, state and local programs.
Energy Resources for State, Local and Tribal Governments
EPA’s State and Local Climate and Energy Program offers free tools, data and technical expertise on energy strategies, including energy efficiency, renewable energy and other emerging technologies, to help state, local and Tribal governments achieve their environmental, energy and economic goals.
Green Power Partnership and Green Power Markets Programs
These EPA programs provide tools and resources to help people understand and engage with green power.
Landfill Methane Outreach Program
This voluntary EPA program works cooperatively with industry stakeholders and waste officials to reduce and avoid methane emissions from landfills. It encourages the recovery and beneficial use of biogas that comes from organic municipal solid waste.
U.S. Department of Energy Biomass, Geothermal, Solar and Wind Programs
These programs offer general information, research, funding and technical assistance.