Generating ToxCast Data
Overview of Generating ToxCast Data from Source to User

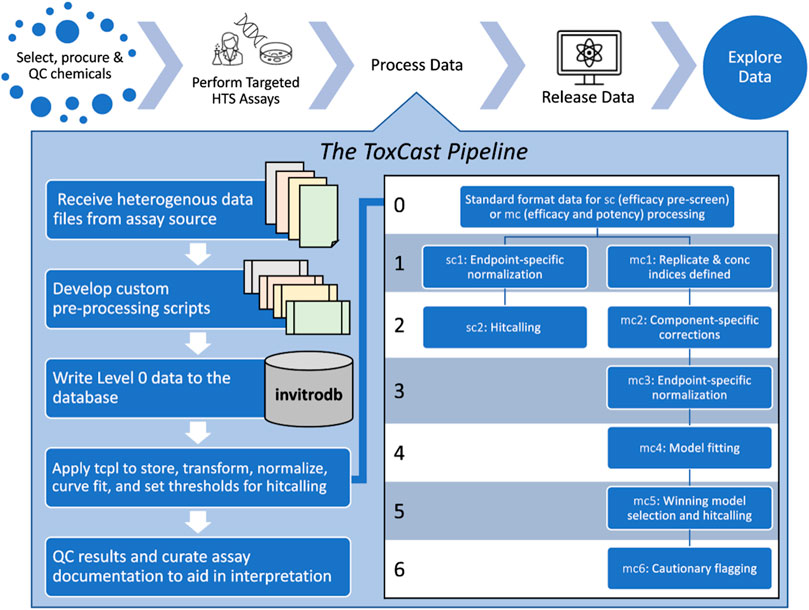
The U.S. Environmental Protection Agency Toxicity Forecaster (ToxCast) program makes in vitro medium- and high-throughput screening assay data publicly available for prioritization and hazard characterization of thousands of chemicals. The assays employ a variety of technologies to evaluate the effects of chemical exposure on diverse biological targets, from distinct proteins to more complex cellular processes like mitochondrial toxicity, nuclear receptor signaling, immune responses, and developmental toxicity. The ToxCast data pipeline (tcpl) is an open-source R package that stores, manages, curve-fits, and visualizes ToxCast data and populates the linked MySQL Database, invitrodb.
This flexible analysis pipeline is capable of efficiently processing and storing large volumes of data. The diverse data, received in heterogeneous formats from numerous vendors, are transformed to a standard computable format and loaded into the tcpl database by vendor-specific R scripts. Once data is loaded into the database, ToxCast utilizes generalized processing functions provided in this package to process, normalize, model, qualify, and visualize the data.