Chemicals Dashboard Help: Basic Search
There are a variety of search capabilities presently available on the dashboard. The basic search can be performed on the homepage by chemical name or identifier, product use category, and assay/gene name. A number of chemical "identifiers" can be searched including chemical name, common name, CAS Number or InChIKey. The search is set up as an EXACT String Search by default (giving a single result) but selecting the Identifier substring search box allows for a larger results set. The results can also be pre-filtered using the checkboxes below the entry box to return only chemical entities that have a single component or exclude isotopically-labeled compounds (e.g. no deuterium- or 13C-labeled compounds).
For all searches, both homepage and in-Dashboard search box, after a brief delay a drop down list of possible matches appears. The mouse or arrow keys + Enter can be used to select preferred choice. A successful chemical search opens the Details page for that chemical, product use and assay / gene searches yield tables of relevant information.
- Chemical Details
- Executive Summary
- Physchem Properties
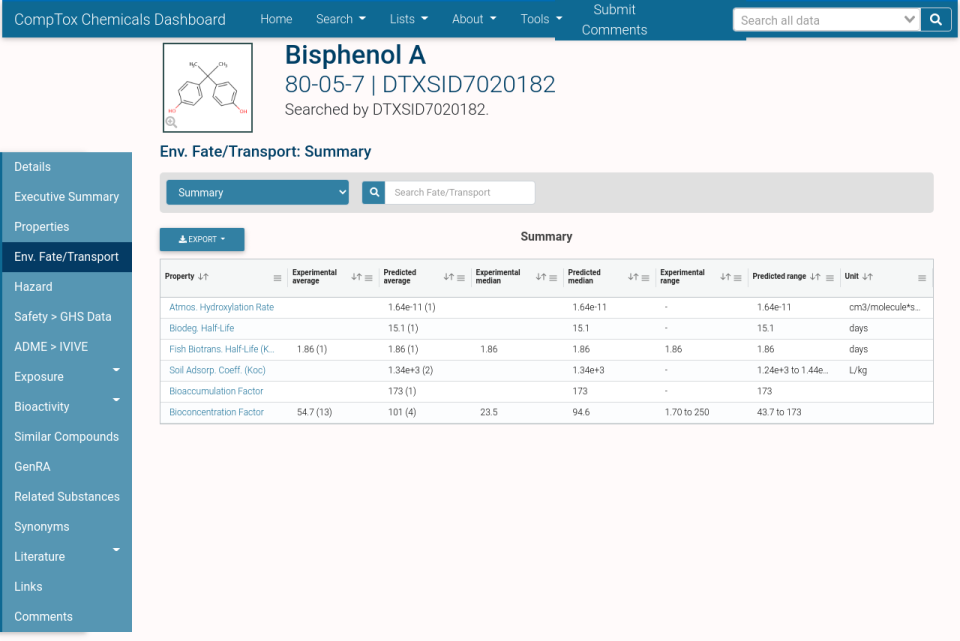
- Environmental Fate/Transport
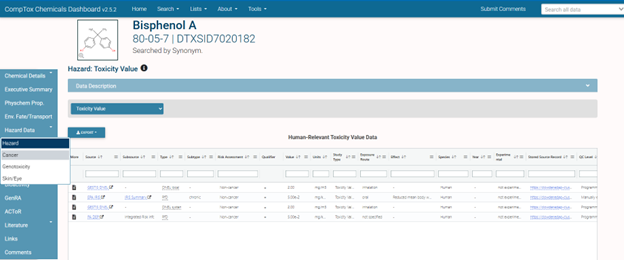
- Hazard
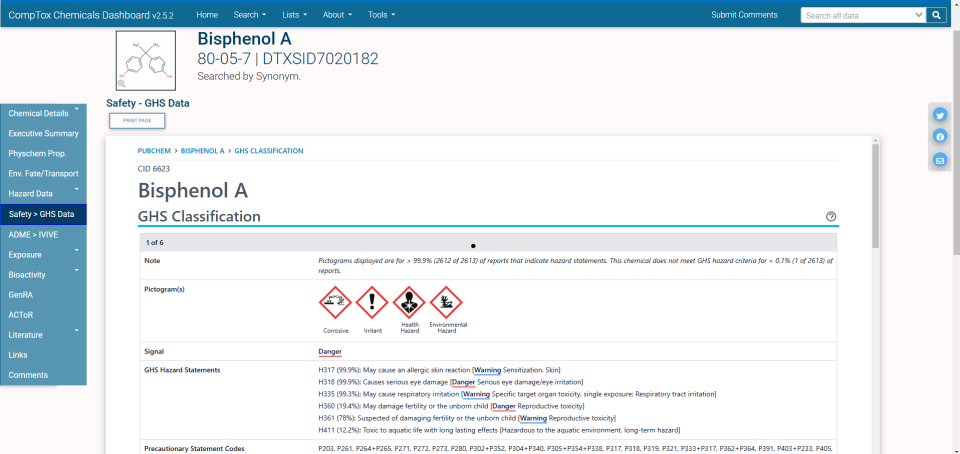
- Safety
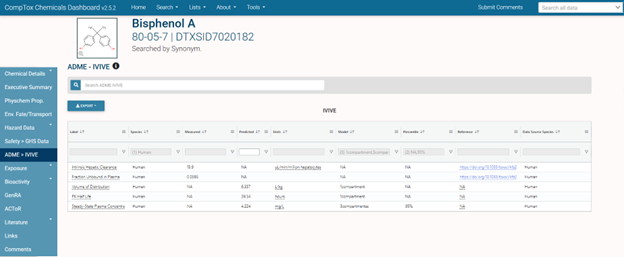
- ADME>IVIVE
- Exposure
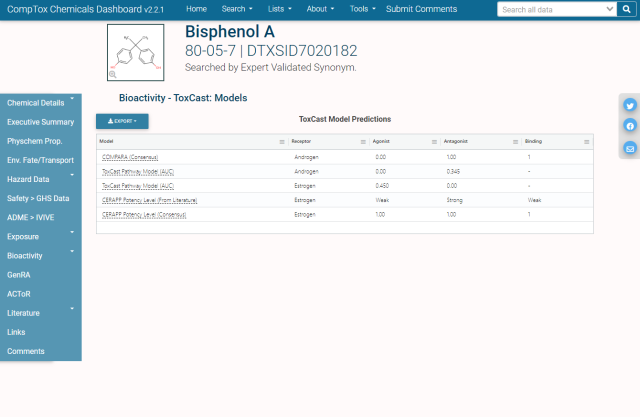
- Bioactivity
- GenRA
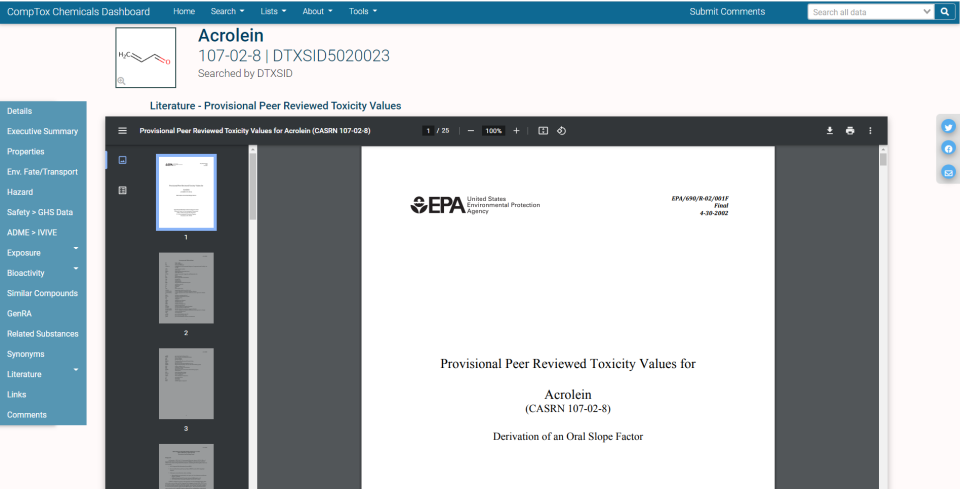
- Literature
- Links
- Comments
Chemical Details
Details
The Details tab provides overview information for the selected substance, including different identifiers, relationships to other substances, QA/QC and other metadata, and a description from Wikipedia, if available. By default, the Wikipedia and Intrinsic Properties sections of the “accordion”, if present, are expanded and the other sections are collapsed, clicking a section heading expands or collapses the section.
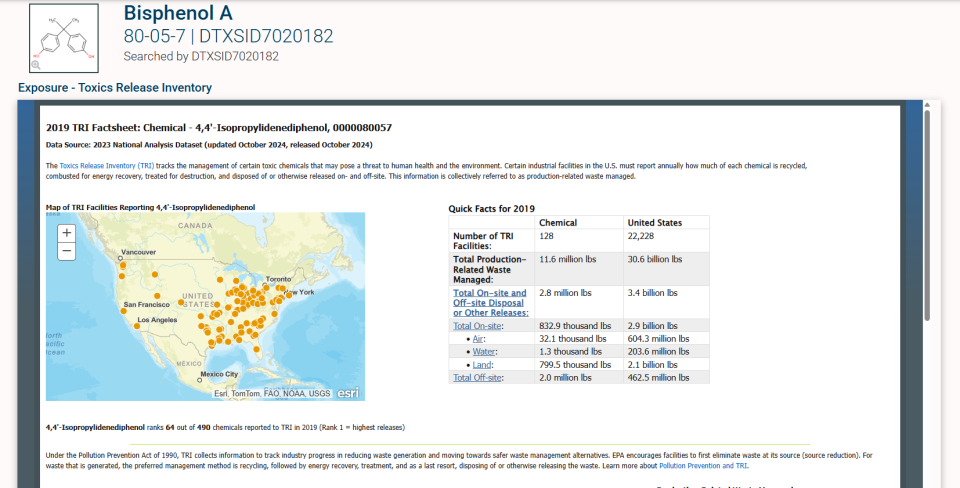
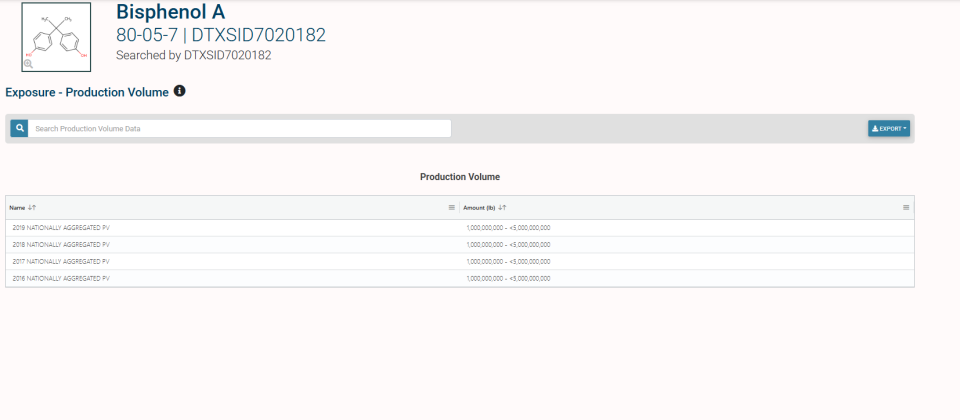
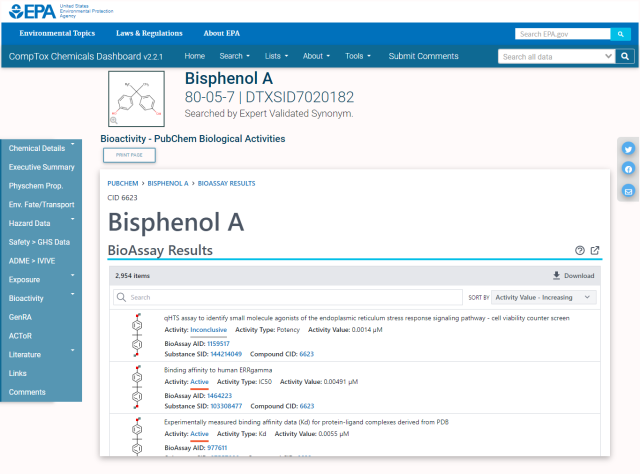
Here is an example of the returned result when "BPA" is searched: Bisphenol A Chemical Result
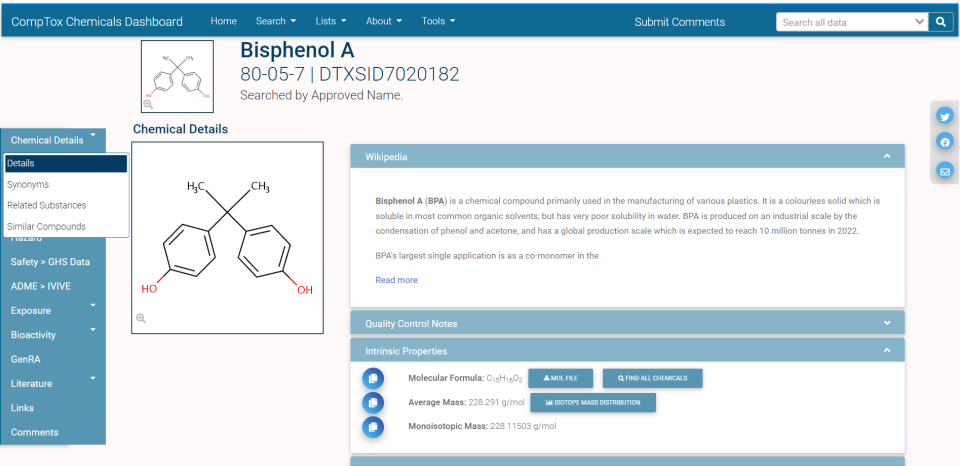
Details tab.
Wikipedia
The Wikipedia section contains a short description of the chemical from its Wikipedia page. Selecting the Read More link on that section opens to the Wikipedia page for the chemical.
Quality Control Notes
The Quality Control Notes section provides information on quality control information for the chemical where applicable.
Intrinsic Properties
For chemicals with a defined structure, the Intrinsic Properties section displays the Molecular Formula, the Average Mass, and the Monoisotopic Mass. The molecular formula component displays the formula for the chemical (e.g. C15H16O2). There is a link for a downloadable Mol file allowing you to load the molecules structure into other software. The Find All Chemicals button provides a table of all chemical substances with the same molecular formula which can be downloaded. The Average Mass component provides the average mass of the chemical in grams per mole. The Isotope Mass Distribution button provides a display of the relative abundance of the isotopes of the chemical along with the mass-to-charge ratio. The Monoisotopic Mass simply displays that value for the chemical.
Structural Identifiers
Various identifiers for the chemical, including:
- IUPAC name
- SMILES structure – note that this is a substance level SMILE structure. This SMILE structure and two others (Mass Spectrometry (MS) ready SMILES, and QSAR ready SMILES (e.g., those used to run OPERA models)) can be downloaded using the batch download
- Full InChI string
- InChIKey (for searching on-line).
There are also links to open a Google search page for the structural skeleton (first part of the InChIKey, or the full structure (full InChIKey).
Linked Substances
The Linked Substances section contains links to tables of related chemicals:
- Same Connectivity - the structural skeleton according to the first part of the InChIKey.
- Mixtures, Components, and Isotopomers - links to other chemicals containing the selected chemical, or in the case of multi-component chemicals (e.g. Perisoxal citrate), other chemicals containing each component, as well as isotopomers.
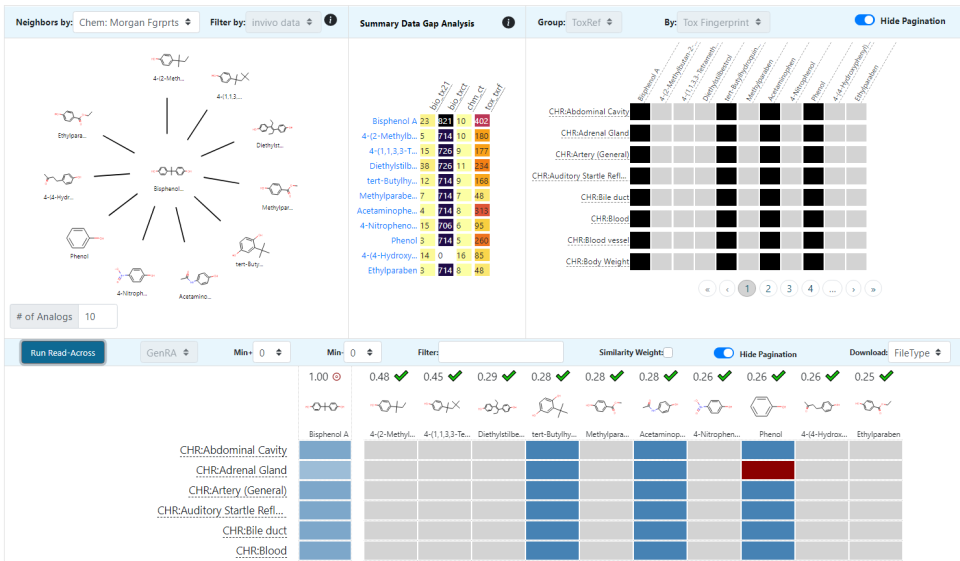
- Similar compounds - a link to similar compounds based on a calculated similarity value, see Similar Compounds for details. This is the same list as the similar compounds tab on the left.
Presence In Lists
The Dashboard includes a database of curated lists of chemicals, this section provides links to lists containing the selected chemical, in Federal, US State, International, and Other categories.
Record Information
The Record Information section contains a citation (with copy-to-clipboard button) that can be used to cite the selected chemical’s page in the Dashboard. It also reports the data quality level for the selected chemical’s data in the Dashboard, with levels from highest to lowest:
- Expert curated, highest confidence in accuracy and consistency of unique chemical identifiers
- Expert curated, unique chemical identifiers using multiple sources
- Programmatically curated from high quality EPA source, unique chemical identifiers have no conflicts in ChemID and PubChem
- Programmatically curated from ChemID, unique chemical identifiers have no conflicts in PubChem
- Programmatically curated from ACToR or PubChem, unique chemical identifiers with low confidence, single public source
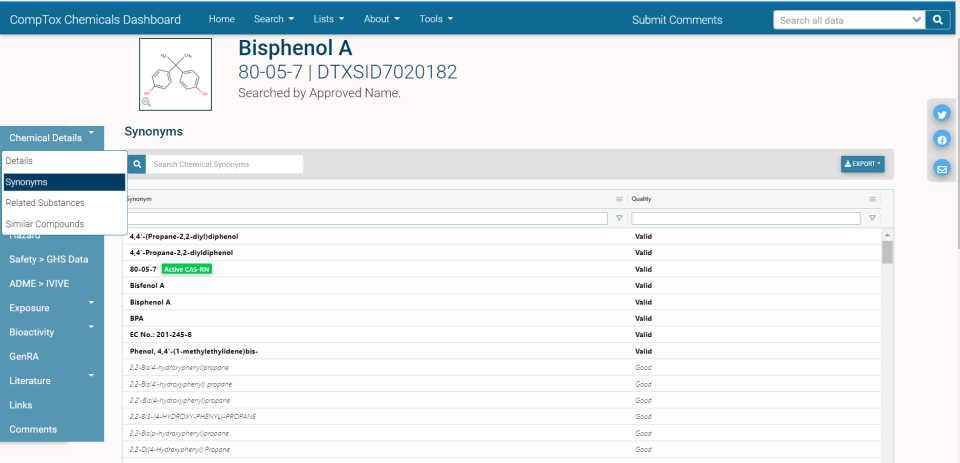
Synonyms
The Synonyms tab provides a curated list of Synonyms with their associated quality (valid, good, other, deleted).
The database contains over a million synonyms obtained from various resources. These are displayed with the relevant quality flags as shown below. Valid Synonyms are those that have been manually curated by members of our curation team. Good Synonyms have been obtained from a variety of sources and using complex workflows for cross-referencing are ranked as being of higher quality than the remaining collection of “Other Synonyms”. The synonyms are not warranted as perfect or complete but are the results of our best efforts.
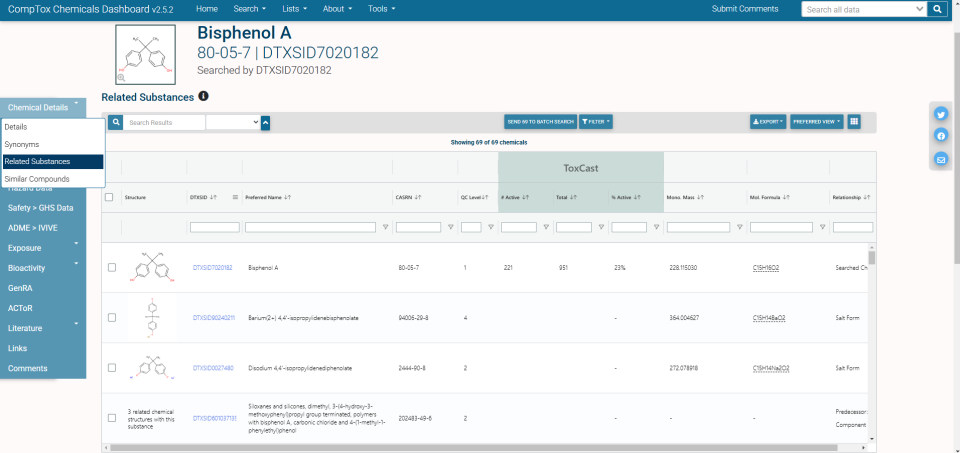
Related Substances
The Related Substances tab provides a chemical list of all chemicals related to the selected chemical.
Relationships include:
- Searched Chemical (self relationship)
- Salt Form
- Monomer
- Polymer
- Predecessor: Component
- Component
- Markush Parent
- Markush Child
- Transformation Parent
- Transformation Product
Note: The Relationship column in tabular view defaults to the far right of the table, the table view may need to be adjusted horizontally to make it visible. Related substance results always include the target chemical as the first result in the table.
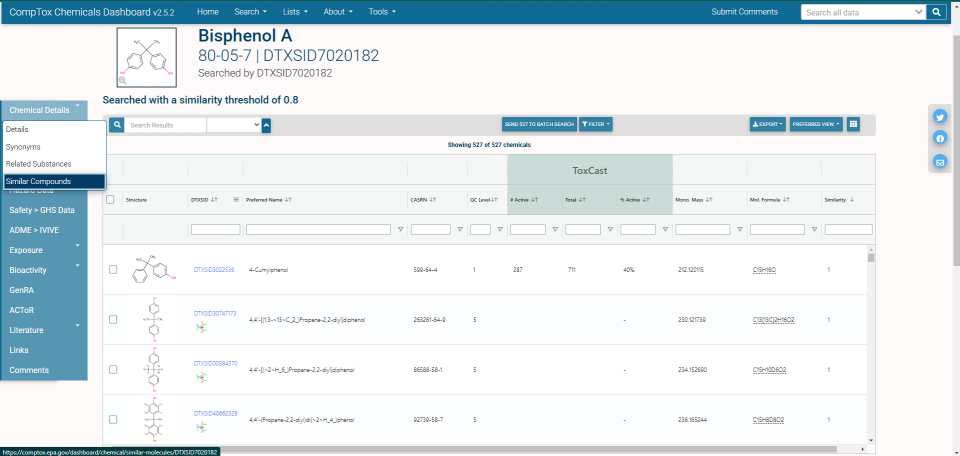
Similar Compounds
The Similar Compounds tab provides a list of chemicals that are similar in structure to the selected chemical, and is based on the Tanimoto similarity search metric with a minimum similarity factor threshold of 0.8. Since the chemicals set is displayed in the usual Table format utilized across the rest of the application the chemicals set can be toggled between table and structure tile mode and, for the case of similarity searches, sorted based on increasing and decreasing similarity score. The resulting set of chemicals can be downloaded in various formats including Excel, comma-separated values (CSV) and SDF formats (generally readable by chemoinformatics tools such as ChemDraw, ACD/ChemSketch and others). The hit list can be filtered in the same way as all other chemical results in terms of filtering out isotopically labeled chemicals, multiple component substances etc.
A chemical can match multiple chemicals with a similarity search match factor of >0.8, for example, see Bisphenol A similarity matches which has over 400 chemicals above that threshold. It is possible to have multiple chemicals with a match factor of 1.0, which might be assumed to be a perfect match but is, rather, an indication of the match of the structure bitstring fingerprint.
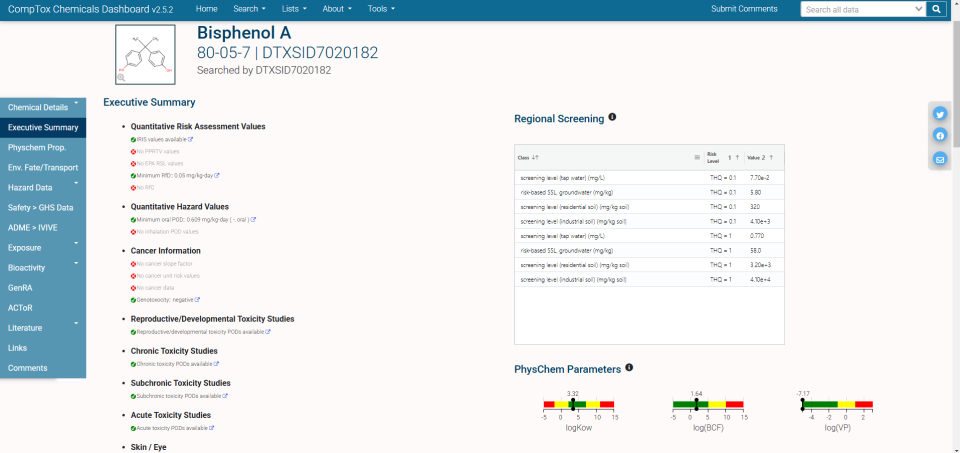
Executive Summary
The Executive Summary tab summarizes the selected chemical’s characteristics and data availability for the selected chemical. Red cross marks and faded text indicate an absence of data. Green check marks and normal text indicate the presence of data. Data summarized includes toxicology, behavior in the environment, safety, carcinogenicity, and Adverse Outcome Pathway (AOP) information.
Some links, like the AOP data, go to external resources, but many, so called “deep links”, guide the user deeper into the Dashboard data itself. Deep links take the user to the Dashboard page where the information referenced in the Executive Summary can be found in detail.
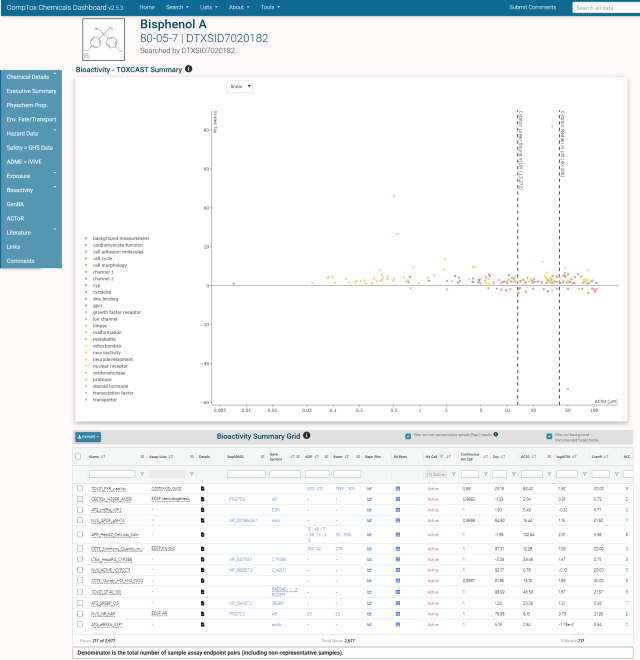
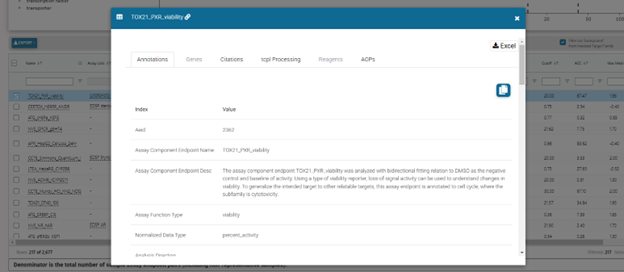
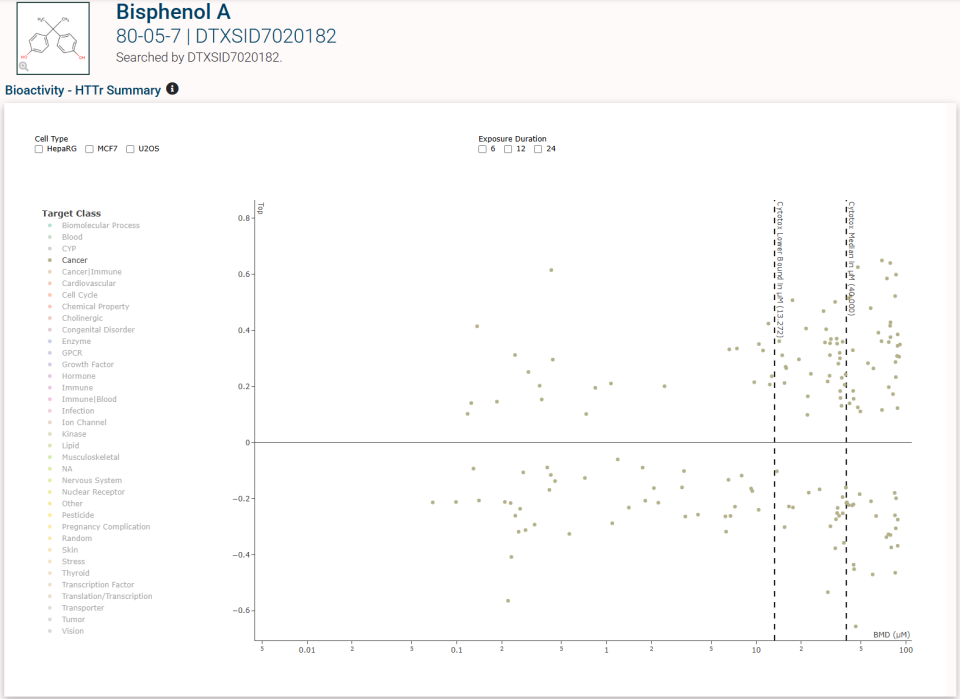
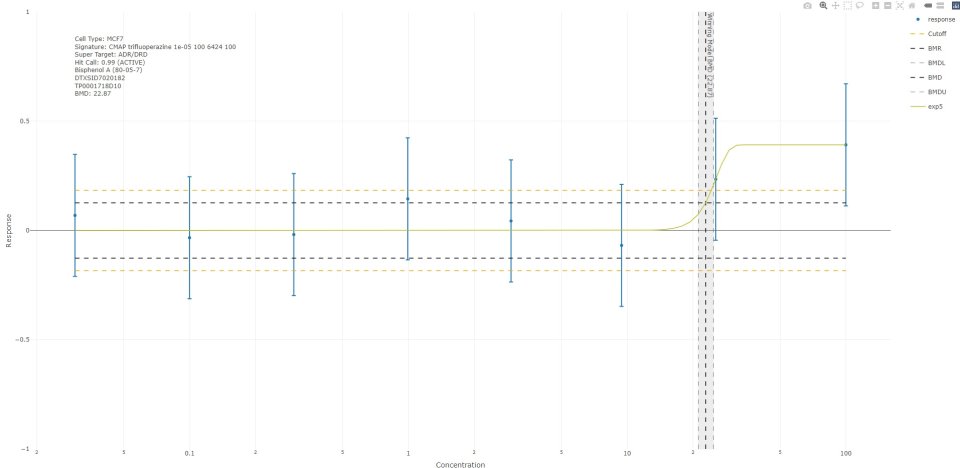
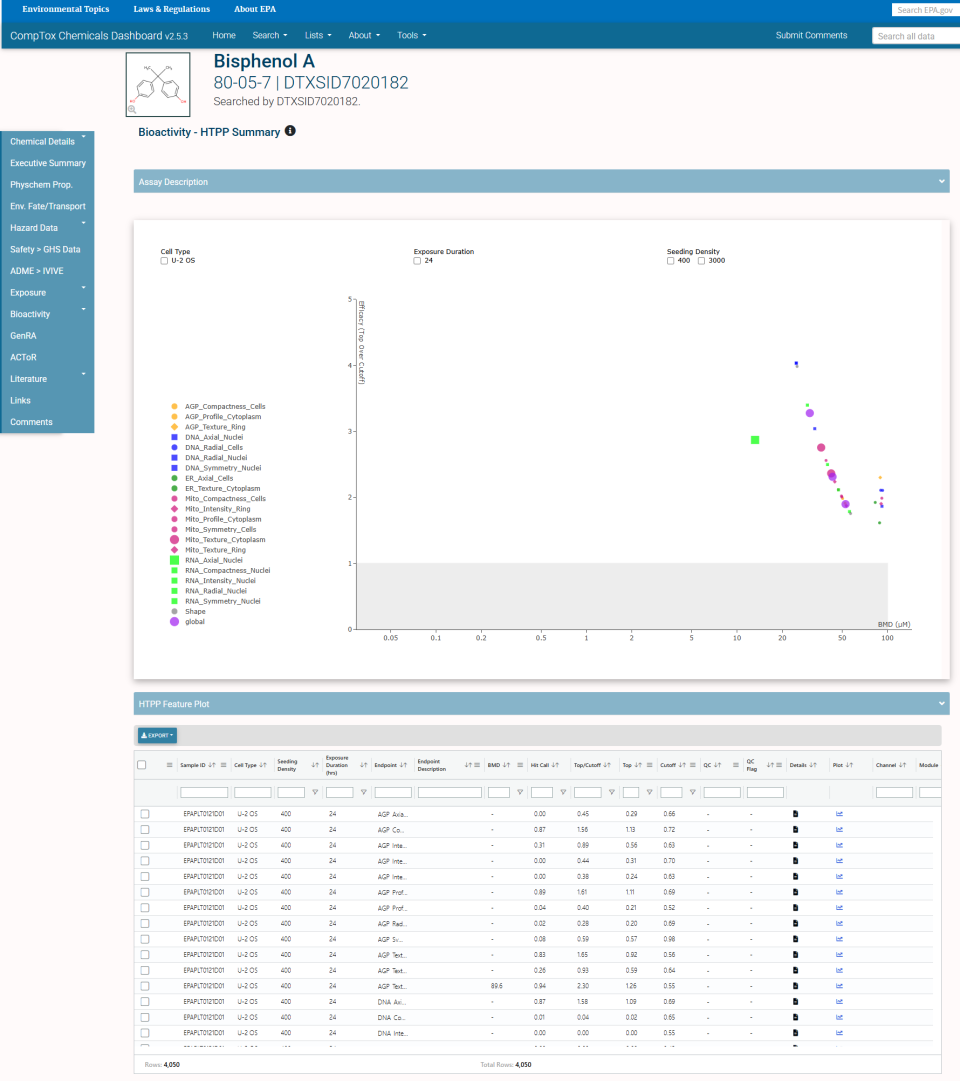
The Executive Summary tab also includes plots of some of the selected chemical’s physical parameters, Point of Departure (POD) ranges for bioassay endpoints, and a summary of TOXCAST data. There is a also a table of “regional screening” levels, levels considered protective of public health in environmental exposure scenarios.
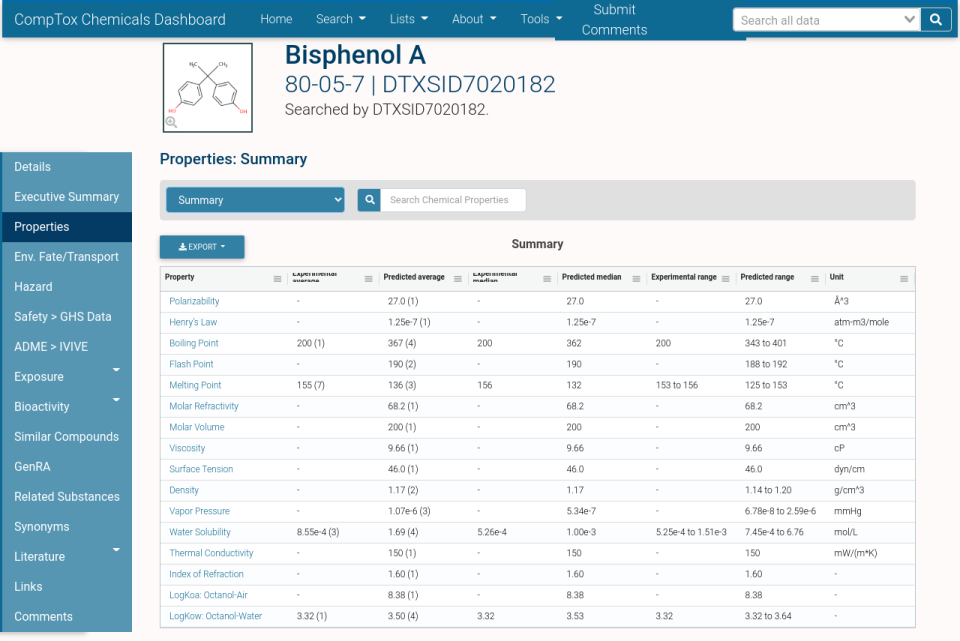
Physchem Properties
The Properties tab provides values for various properties of the selected chemical, like Boiling Point, Index of Refraction, Density, etc. Both experimental (measured in a laboratory) and predicted (by mathematical / computer models) values are available.